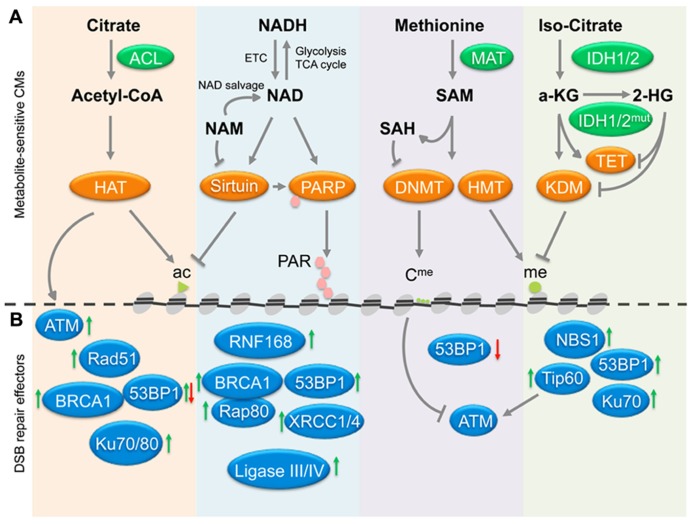
FIGURE 1.
Cross-talk between metabolites, chromatin and DSB repair. (A) The deposition of chromatin marks is influenced by metabolites, which function as cofactors or substrates for the indicated chromatin modifiers (CMs). Central pathways affecting histone acetylation, deacetylation, PARylation, and histone/DNA methylation and demethylation are shown, arrows indicate positive regulation/deposition of chromatin marks, blunted arrows depict negative regulation/removal of chromatin marks. (B) Chromatin marks deposited or removed through pathways in (A) have been implicated in the modulation of the recruitment of the indicated repair factors, suggesting a possible link between metabolites and DSB repair. Green arrows indicate that a given chromatin modification results in increased recruitment/activation of the indicated repair factors, red arrows depict impaired activation/recruitment in the presence of the same modification. See Table 1 for a detailed list of modifiers and modifications involved in DSB repair. In addition to chromatin, the HAT Tip60 can acetylate and activate the central DDR mediator ATM kinase (gray arrows), whereas ATM activity is negatively affected by DNA methylation (blunted gray arrow). Ac, acetylated histone; me, methylated histone; Cme, methy-cytosine; PAR, poly-(ADP-ribose); ETC, electron transport chain; HAT, histone acetyl transfrease; HMT, histone methyltransferase; KDM, lysine demethylase. See text for enzyme and metabolite abbreviations.