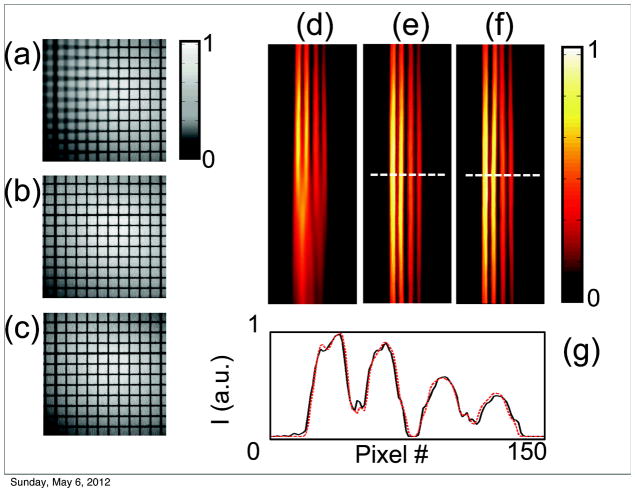
Figure 3.
(a–c) Phantom grid reconstruction in white light mode. A flat black and white grid was tilted along one horizontal axis to produce images with only part of the grid in focus. (a) A single frame from a stack of partial in focus images. (b) An image reconstruction of all the in focus components obtained from the stack of images in (a). The same grid with no tilt was used as a reference (c). To correctly compare the processed image (b) to the reference (c), a stretching factor, perpendicular to the tilting axis, was applied. (d–g) Phantom tubes in fluorescent mode. (d) A single image from a stack of fluorescent images. As for the grid, the tubes were tilted along one horizontal axis to provide out of focus components. (e) The reconstructed fused image. (f) A reference image acquired with zero tilting. (g) A signal profile along one line to compare the fluorescent distribution of the reconstructed and reference image.