Figure 1.
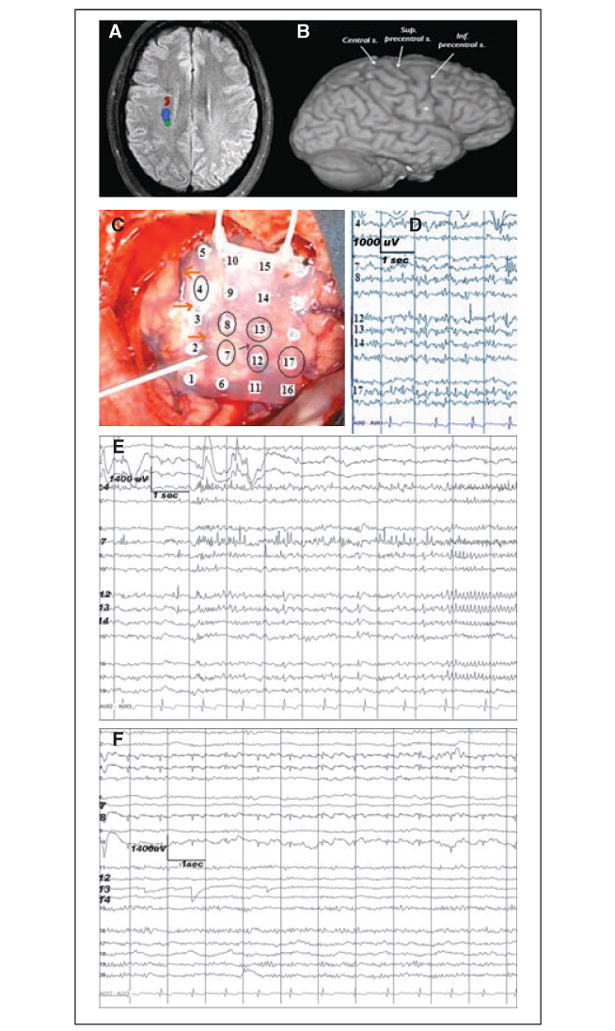
Neuroimaging and ECoG studies showing the topographic relationship among the epileptogenic dysplastic lesion, corticospinal tract, and the eloquent motor cortex. (A) fMRI showing the location of the subcortical motor (dark red and blue) and somatosensory fibers. Descending fibers of the corticospinal tract (dark red) are in proximity to the dysplastic lesion (arrow). (B) At the cortical level, the center of the lesion (dot) is located close to the precentral sulcus. (C) Preresection ECoG recording done with a 20-contact grid placed over the right frontal (contact 16 most anterior-inferior, contact 5 most posterior-superior). Circled are the contacts showing epilepti-form/epileptic activity. The reference is contralateral mastoid. The surgeon is pointing toward the central sulcus (also empha-sized by the orange arrows). The thin black arrow points towards the precentral sulcus. The recording was done using a 32-channel digital EEG machine (XLTEK/NATUS, Oakville, ON, Canada); low frequency filter = 1 Hz, high frequency filter = 70 Hz. (D) Preresection ECoG. Multifocal spikes are seen on both sides of the precentral sulcus: anterior (contacts 12, 13, and 17) and posterior (contacts 7, 8, and 4) to it. (E) Preresection ECoG. Focal ictal onset at contacts 7 and 4, within the precentral gyrus. ( F ) Postresection ECoG shows no epileptiform or epileptic activity. The recording is done via a 20-contact grid with the reference electrode on the contralateral mastoid.
Epilepsia © ILAE
