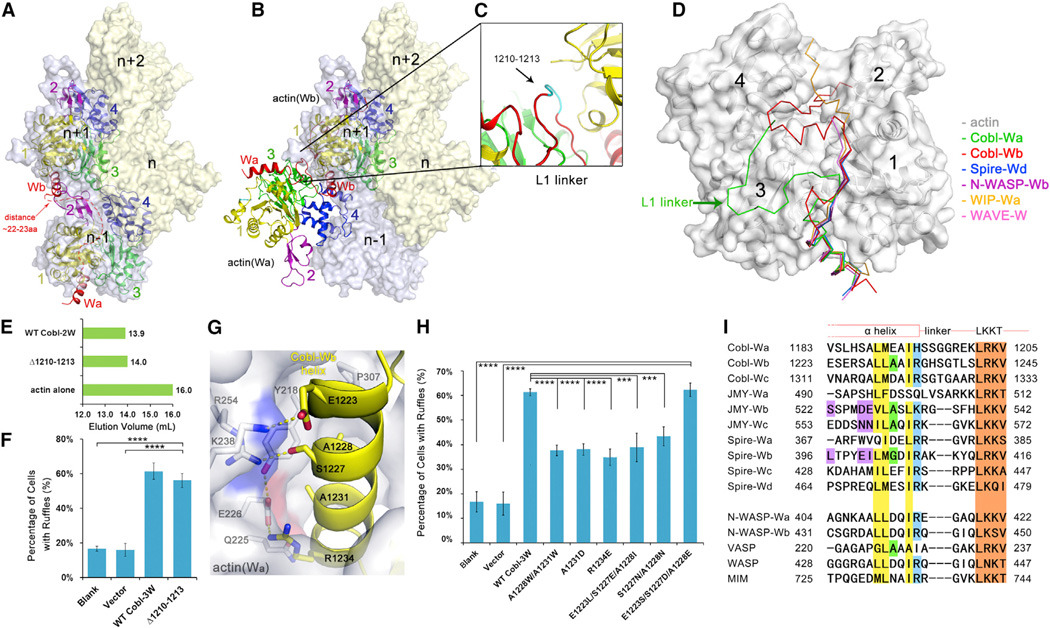
Figure 4. The Observed Conformation of Actin-Cobl-2W Is Biologically Relevant.
(A) F-actin structure from fiber diffraction, with two neighboring longitudinal actin subunits highlighted. The number of residues required to span the W-binding sites on two neighboring longitudinal actin subunits was estimated using the structure of actin-WIP-Wa (PDB 2A41) as a reference and shown as a red dashed line.
(B) Superposition of actin-Cobl-2W structure onto F-actin.
(C) The extensively curled L1 linker.
(D) Comparison of known actin-W structures. The PDB codes are Spire-Wd (3MN5), N-WASP-Wb (2A3Z), WIP-Wa (2A41), and WAVE-W (2A40).
(E) Elution profiles of Δ1210–1213.
(F) The mutant Δ1210–1213 is fully active in membrane ruffle induction activity. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three to five independent experiments (****p < 0.001 in two-tailed Student’s t test).
(G) The actin(Wa)-Wb interface.
(H) Comparison of ruffle induction activities for designed mutations. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three to five independent experiments (****p < 0.001; ***p < 0.005 in two-tailed Student’s t test).
(I) Sequence alignment of W domains from tandem W-domain-containing actin filament nucleators and from nucleation-promoting factors. GenBank sequence accession numbers are AAP74341 (Cobl), Q9U4F1 (Spire), AAI30625 (JMY), O00401 (N-WASP), P50552 (VASP), P42768 (WASP), and O43312 (MIM). The LKKT-related motifs are colored in brown. Residues corresponding to the hydrophobic side of the N-terminal α helix, A1231, and R1234 in Cobl-Wb are in yellow, green, and blue, respectively. The key sequence differences on the hydrophilic side of the N-terminal α helix in Spire-Wb, JMY-Wb, and Wc are highlighted in purple.
See also Figures S3, S4, S5, and S6.