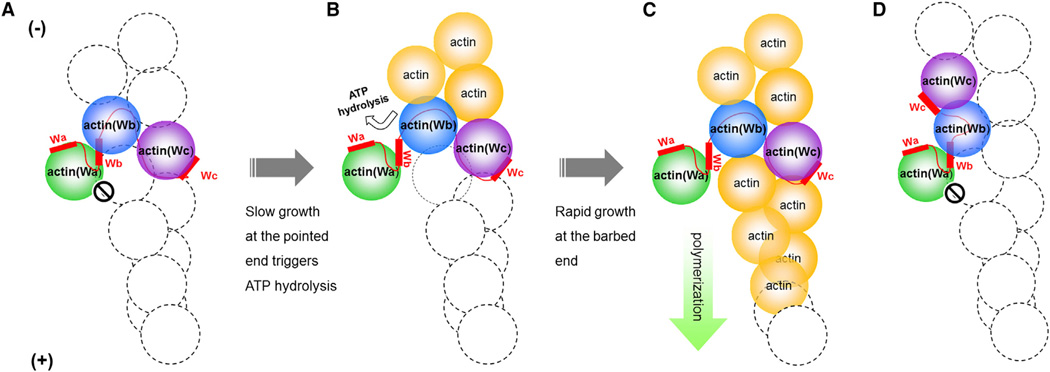
Figure 6. Proposed Models of Actin Filament Nucleation and Polymerization Mediated by Tandem W Domains.
(A–C) Proposed model of Cobl-mediated actin nucleation. The actin-Cobl nucleus allows the pointed-end but not the barbed-end growth (A). Slow growth at the pointed end triggers ATP hydrolysis in actin(Wb). The bound Cobl-Wb is expulsed from actin(Wb), and the steric hinderance imposed by actin(Wa) is released (B). Rapid growth of actin filament proceeds at the barbed end, and slow depolymerization at the pointed end eventually releases the bound Cobl into solution (C).
(D) Proposed nucleus of actin-JMY.