Fig. 7.
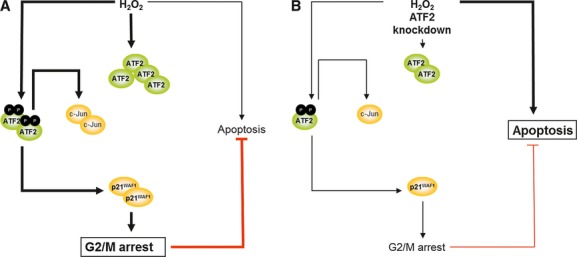
Mechanistic model of the TE7 cell response to H2O2 and to H2O2 plus ATF2 knockdown. (A) H2O2 exposure causes DNA damage and consequently the activation of ATF2 via phosphorylation on threonine residues 69 and 71. This transcription factor induces the transcription of p21WAF1 and c-Jun. As ATF2 induces the G2/M growth arrest via p21WAF1, ATF2 thereby inhibits apoptosis. (B) The combination of H2O2 stress with the knockdown of ATF2 leads to reduced ATF2 protein level, causing a lesser amount of c-Jun and, most notably, of p21WAF1. Consequently, G2/M arrest is reduced, but apoptosis reinforced.
