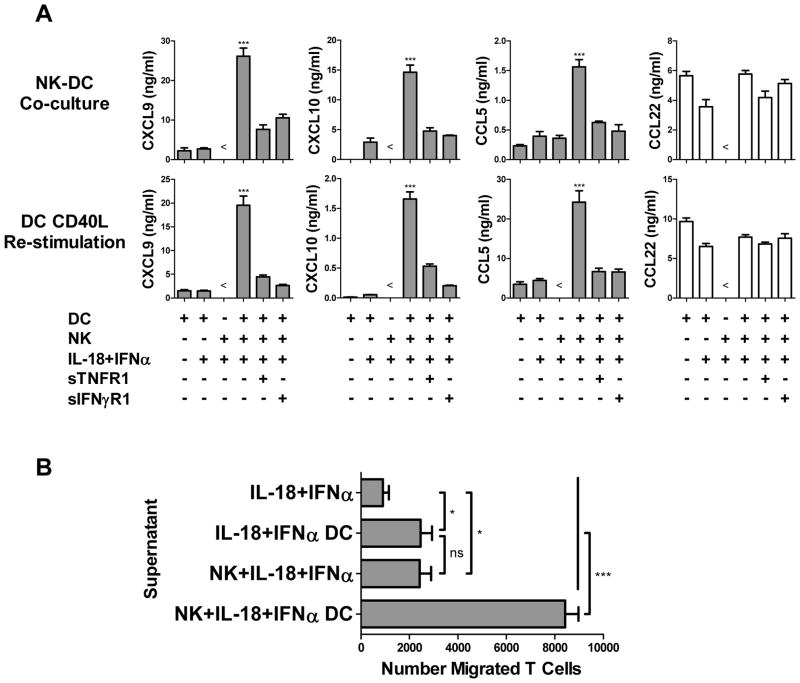
Figure 4.
IL-18-primed NK cells induce DC production of Teff cell-recruiting chemokines, promoting Teff cell attraction. NK cells were added to autologous day 6 DCs (1:2 NK:DC ratio) in the presence of IL-18 and IFNα. After 48 h, co-culture supernatants were harvested for analysis and chemotaxis experiments, and DCs were harvested, washed, depleted of NK cells, and re-stimulated with CD40L for 24 h. (A) CXCL9, CXCL10, CCL5, and CCL22 levels in supernatants of untreated immature DCs (iDCs) or DCs exposed to IL-18/IFNα with or without autologous NK cells, in the additional presence or absence of soluble TNF (sTNFR1) or IFNγ (sIFNγR1) decoy receptors, after 48 h co-culture (top) or following harvesting, washing, NK cell depletion, and 24 h CD40L stimulation (bottom). (B) Migration of effector CD8+ T cells (see Materials and Methods for generation) toward supernatants collected from 48 h cultures of IL-18/IFNα alone, NK cells treated with IL-18/IFNα, or DCs exposed to IL-18/IFNα with or without autologous NK cells. Data recorded as mean (± SD) in triplicate cultures from one representative experiment of three performed, all yielding similar results. ***p<0.001, *p<0.05, ns: p>0.05 compared to indicated groups or compared to all groups when not specifically indicated. < indicates levels were below the limit of detection of the assay.