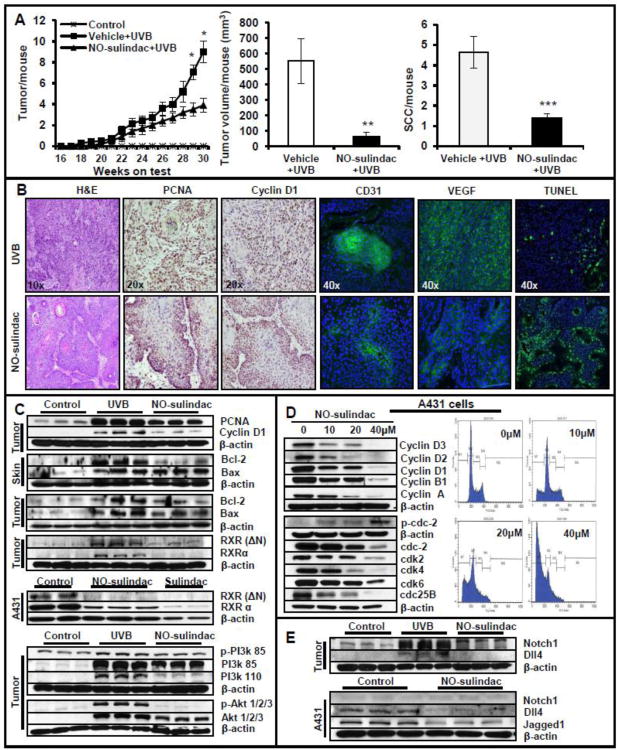
Figure 1.
NO-sulindac reduces UVB-induced skin tumorigenesis by inhibiting proliferation, angiogenesis and by inducing cell cycle arrest/apoptosis via Notch/RXR-PI3K/Akt axis. (A) Data showing tumors/mouse, tumor volume/mouse (mm3) and SCCs/mouse; (B) histology, immunostaining for PCNA, cyclin D, VEGF and CD31 & TUNEL staining; (C) western blot analysis showing expression of PCNA, cyclin D1, Bax and Bcl-2 in tumors and tumor-adjacent skins. Shown here also is the expression of RXRs in murine SCCs and human A431 cells, & PI3K/Akt proteins in murine tumors; (D) western blot analysis showing expression of cyclins/cyclin dependent kinases and Flow cytometry analysis of A431 cells treated with NO-sulindac; (E) western blot analysis showing expression of Notchl, DII4 and Jaggedl in murine tumors and in A431 cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005 and ***P < 0.001.