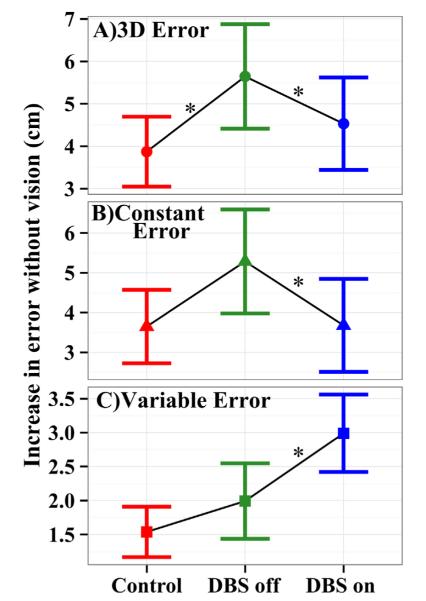
Fig. 5.
Difference in error across the vision conditions (no vision minus vision). Increasing values indicate increasingly larger errors in the no vision than vision condition, implying increased difficulty in localizing the limb using proprioception. Whisker bars indicate 95% confidence intervals across subjects. Asterisks indicate a significant difference between groups (p < 0.05). (A) 3D errors show disproportionately increased localization errors for STN DBS Off patients than control subjects when vision is occluded; this deficit is partially reversed when STN DBS is turned on. (B) Constant errors show the same pattern although the group difference is significant only for STN DBS On versus Off. (C) Variable errors show a small increase for STN DBS Off patients over that of control subjects, which is exacerbated by switching DBS on.