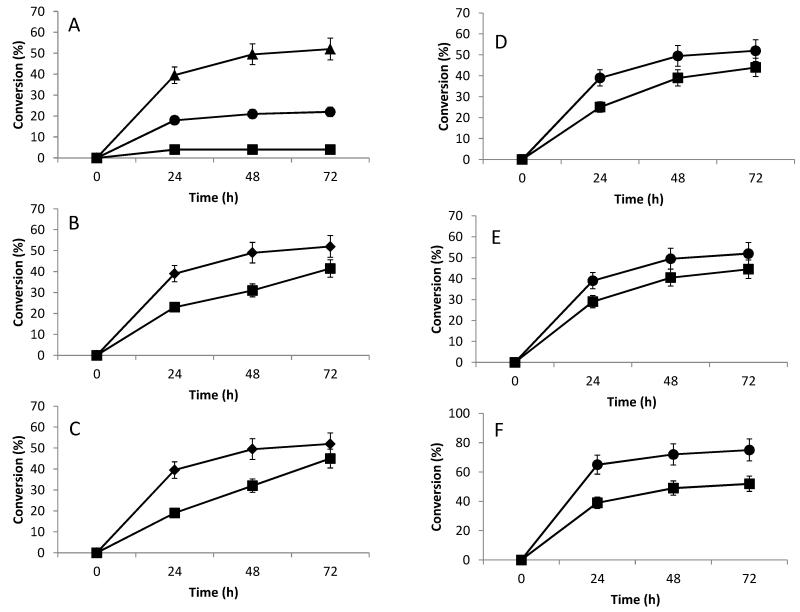
Figure 2.
Optimization of conditions for conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp using immobilized 2-OST, C5-epi and AST-IV. A. Effect of different substrate concentrations on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: 0.1 mg/ml ( ); 1.0 mg/ml (
); 1.0 mg/ml ( ); 10 mg/ml (
); 10 mg/ml ( ). B. Effect of amount of PAPS on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: 40 μM (
). B. Effect of amount of PAPS on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: 40 μM ( ); 200 μM (
); 200 μM ( ). C. Effect of different methods of reaction on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: over 72 h and separate treatment of C5-epi (
). C. Effect of different methods of reaction on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: over 72 h and separate treatment of C5-epi ( ); normal treatment (
); normal treatment ( ). D. Effect of separate epimerization reaction on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: three-step treatment (
). D. Effect of separate epimerization reaction on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: three-step treatment ( ); normal treatment (
); normal treatment ( ). E. Effect of types of different reactors on the conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: column reactor (
). E. Effect of types of different reactors on the conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: column reactor ( ); batch reactor (
); batch reactor ( ). F. Effect of amount of enzymes on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: 150 μg/ml (
). F. Effect of amount of enzymes on conversion of NSNAH to NSNA2SHp: 150 μg/ml ( ); 1500 μg/ml (
); 1500 μg/ml ( ). Error bars associated with analytical method are shown.
). Error bars associated with analytical method are shown.