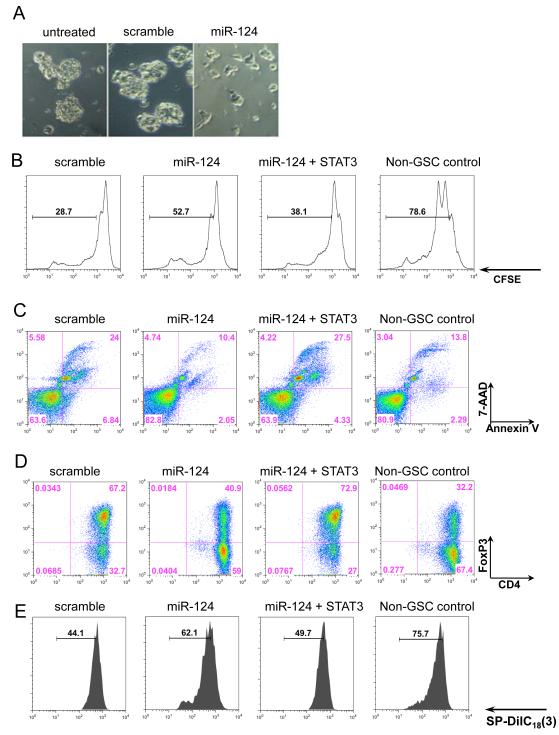
Figure 2.
miR-124 reverses glioma-mediated immunosuppression. (A) The gCSC phenotype was markedly altered by miR-124, as photographed 48 hours after transfection. (B) T-cell proliferation was detected by flow cytometry analysis with CFSE staining after 3 days of treatment with medium alone, gCSC-scramble-transfected conditioned medium, gCSC-miR-124-transfected conditioned medium, or gCSC-miR-124 + STAT3-transfected conditioned medium. miR-124 up regulation caused a reversal of inhibition in T-cell proliferation compared with the gCSC-scramble-transfected conditioned medium. STAT3 overexpression restored gCSC inhibition on T-cell proliferation. (C) T-cell apoptosis was measured by the percentage of annexin V+ 7-AAD+ cells. Similarly, miR-124 up regulation decreased gCSC-induced T-cell apoptosis, whereas STAT3 overexpression reversed the miR-124 effect. (D) T-cells were analyzed on the basis of CD4 and FoxP3 expression levels, by flow cytometry analysis. Up regulation of miR-124 caused a decline in Treg induction compared with the scrambled gCSC control, and STAT3 addition restored the ability of the gCSCs to induce Tregs. (E) The functional suppressive activity of FoxP3+ Tregs induced in (D) was verified by autologous coculture with CD4+ T-cells. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results, and one representative set of data is shown.