Fig. 6.
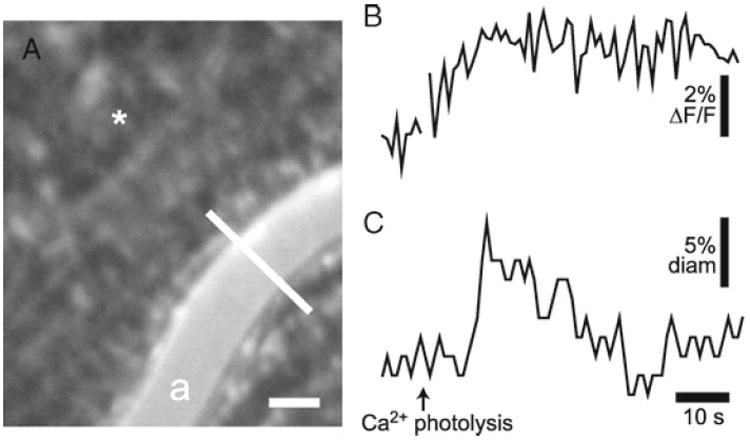
Glial-evoked dilation of retinal arteriole. (a) Confocal image of the retina, showing OGB-labeled glial cells and an arteriole (a) labeled with dextran rhodamine B isothiocyanate. The luminal diameter of the arteriole is monitored with confocal line scans (the white line across the vessel). Asterisk indicates the site of caged Ca2+ photolysis; scale bar, 25 μm. (b) Glial Ca2+ fluorescence measured near the arteriole. Photolysis of caged Ca2+ evokes a glial Ca2+ increase. (c) The luminal diameter of the arteriole. Photolysis evokes a transient increase in vessel diameter.
