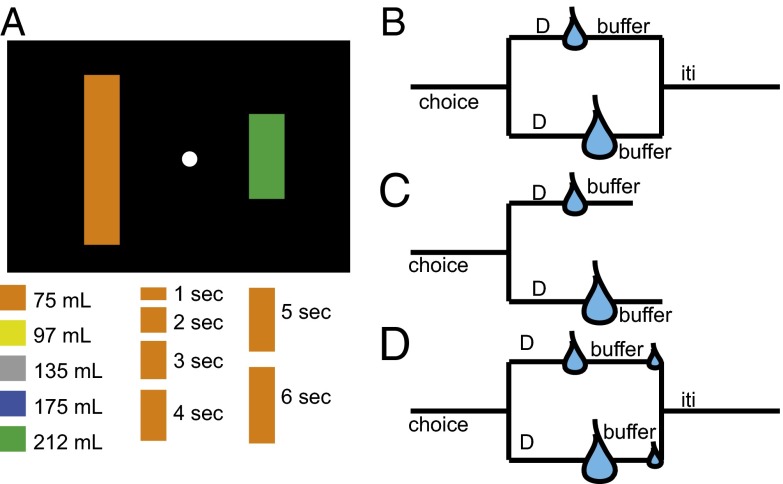
Fig. 1.
Schematic of tasks used in this study. (A) Illustration of display. On each trial, two vertically oriented colored bars appeared to the left and right of a fixation point. The height of each bar indicates the delay until reward for that option. Both prereward delays were chosen randomly from a range of 0–6 s for all versions of the task, indicated by option height (Lower). Color indicates the reward size (Lower). Two bars were chosen randomly for each trial. (B) In the standard intertemporal choice task, postreward buffer duration is adjusted (from 0 to 6 s) so that total trial duration is equated regardless of choice. In the random buffer task, postreward buffer duration is chosen randomly from a uniform distribution (0–6 s). (C) In the constant buffer task, buffers are the same regardless of choice. (D) In the second-reward task, buffers are adjusted (as in the standard task), but a second, small reward is given at the end of the buffer to draw attention to the delay immediately before it. Tasks were run in different weeks to reduce possible interference between tasks.