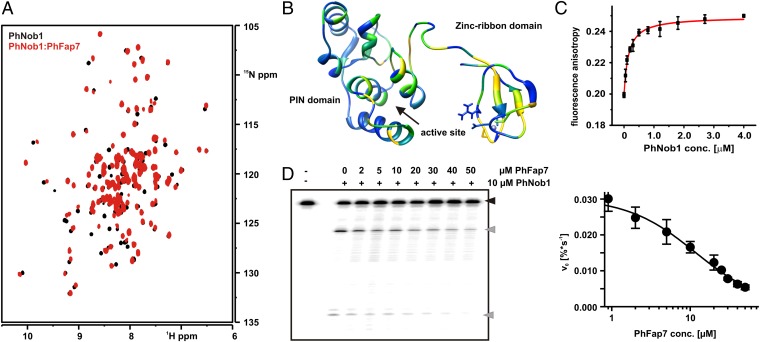
Fig. 4.
PhFap7 binds to PhNob1 and inhibits the D-site cleavage activity of PhNob1. (A) Overlays of HSQCs of 15N-labeled PhNob1 (black) and bound to PhFap7 (red). (B) Mapping of chemical shift changes induced by PhFap7 on the structure of PhNob1. Yellow corresponds to large, green to intermediate, and blue to no chemical shift changes. (C) Determination of the PhFap7:PhNob1 affinity by fluorescence anisotropy titrations. (D) D-site RNA cleavage by PhNob1 in the absence and presence of PhFap7 analyzed by denaturing PAGE (Left). A black arrow indicates uncleaved substrate, gray arrows cleavage products. D-site RNA cleavage velocity of PhNob1 as a function of PhFap7 concentration (Right).