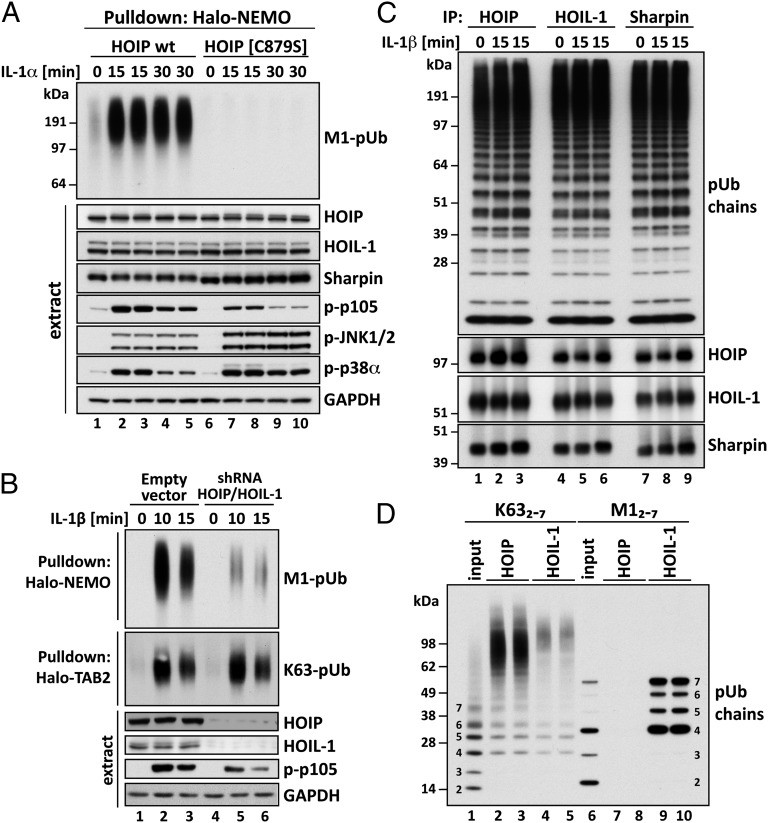
Fig. 4.
Studies on the activity, pUb-binding properties, and role of LUBAC. (A) MEFs from mice expressing either wild-type (wt) HOIP or the HOIP[C879S] mutant were stimulated with 5 ng/mL IL-1α for the times indicated. M1-pUb chains captured from the cell extracts with Halo-NEMO were identified by immunoblotting with a specific antibody (Top). Cell extracts (20 μg protein) were immunoblotted with the antibodies indicated (Bottom seven subpanels). (B) IL-1R cells stably expressing shRNAs specific for HOIP and HOIL-1, or an empty control vector, were stimulated with 5 ng/mL IL-1β and pUb chains captured from extracts with Halo-NEMO or Halo-TAB2. The captured M1-pUb (Top) and K63-pUb chains (Top, second subpanel) were identified by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. Aliquots of the extracts (20 μg protein) were also immunoblotted with the antibodies indicated (Bottom four subpanels). (C) IL-1R cells were not stimulated or stimulated for 15 min with 5 ng/mL IL-1β. The cells were lysed without iodoacetamide to prevent the inactivation of LUBAC, which was then immunoprecipitated from the extracts with anti–HOIL-1, anti-Sharpin, or anti-HOIP. The M1-pUb chains formed after 60 min by LUBAC were examined by immunoblotting. The immunoprecipitates were also immunoblotted for HOIP, HOIL-1, and Sharpin. (D) Full-length GST-HOIP and GST-HOIL-1 were mixed with K63-Ub or M1-Ub oligomers, and, after capture on glutathione-Sepharose, the pUb-oligomers bound to each protein were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-ubiquitin. Lanes 1 and 6 show, respectively, the K63-pUb oligomers and M1-pUb oligomers used. Lanes 2–5 show the K63-pUb chains and lanes 7–10 the M1-pUb chains captured by each protein.