Figure 3. p40phox−/−x Rag1−/−mice show increased susceptibility to anti-CD40-induced colitis.
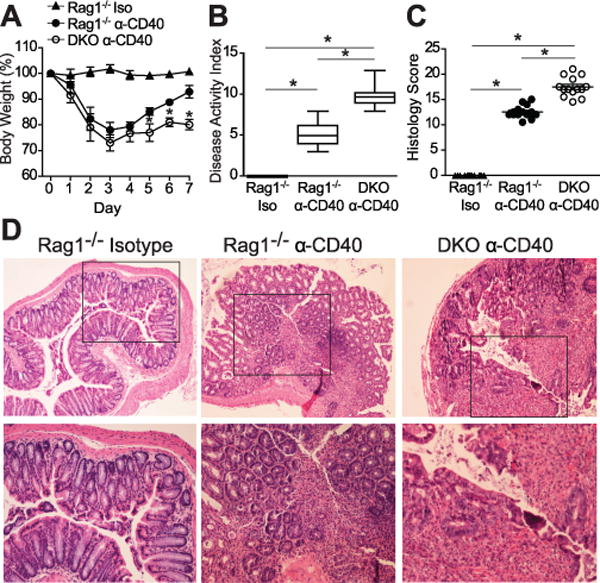
(A) Age- and weight-matched mice were injected i.p. with either anti-CD40 monoclonal depletion antibody (Rag1−/− and DKO mice) or isotype control (Rag1−/− Iso) on day 0. Changes in body weight were monitored daily for 7 days (n = 24 per group; *p < 0.01 between DKO and Rag1−/− mice injected with anti-CD40). (B) Disease activity index was determined on day 7 by scoring hunching, wasting, stool consistency, and colon thickness. Significance was determined by a two-sided Wilcoxon rank sum test; the test rejected the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level (n = 24 per group; *p = 0.0095). (C) Colonic tissue sections were blindly scored for inflammation on day 7. Grading parameters include extent of epithelial hyperplasia, goblet cell depletion, lamina propria infiltration, and epithelial cell damage (n = 14 per group; Rag1−/− average = 12.8 ± 0.5 and DKO average = 17.5 ± 0.5; *p < 0.001). (D) Representative colon sections stained by H&E (top panel: 10X magnification, bottom panel: 20X magnification). Unless otherwise noted, significance was determined using Student’s t test. For all panels, data were generated from four independent experiments.
