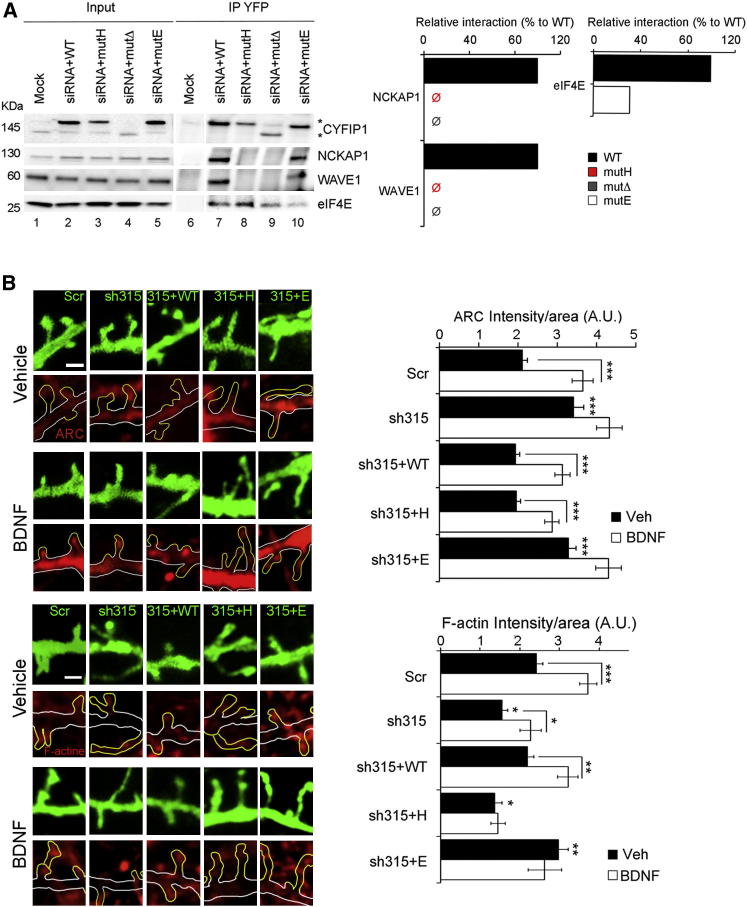
Figure 4.
CYFIP1 Deficiency or Mutations Affecting Interaction with eIF4E or NCKAP1 Alter Synaptic ARC and F-Actin
(A) Dissection of the CYFIP1 interactions with NCKAP1 (mutΔ and mutH) or with eIF4E (mutE). Left panel: IP for YFP-CYFIP1 WT or mutants in HEK293T cells silenced for endogenous CYFIP1. Lane 1, input (1/50) from mock-transfected cells; lanes 2–5, input CYFIP1 siRNA with RNAi-resistant CYFIP1 WT, mutH, mutΔ, or mutE (1/50); lane 6, YFP-IP with mock-transfected cells; lanes 7–10, YFP-IP for WT, mutH, mutΔ, or mutE-CYFIP1. Asterisks indicate exogenous CYFIP1. Central panel: quantification of CYFIP1-NCKAP1 and CYFIP1-WAVE1 as percentage of WT (black) for mutH (red) and mutΔ (gray). Right panel: quantification of CYFIP1-eIF4E as percentage of WT (black) for mutE (white), see also Napoli et al. (2008).
(B) Upper panels: CYFIP1 deficiency or mutations affecting the interaction with eIF4E or NCKAP1 alter synaptic ARC and F-actin levels. Panels show representative dendritic sections transfected with scrambled or Cyfip1 shRNA (F-GFP, upper panels) and stained for ARC (red, lower panels) in vehicle or BDNF-treated neurons. Spines are highlighted in yellow. Scale bar represents 1 μm. Histogram represents the ARC immunosignal normalized to the spine area for neurons transfected as indicated on the x axis and treated with vehicle (black) or BDNF (white) (at least n = 150, two-way ANOVA with Holm’s post hoc test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). Lower panels: as above for F-actin (at least n = 50, two-way ANOVA with Holm’s post hoc test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). Bars represent mean ± SEM.
See also Figure S4.