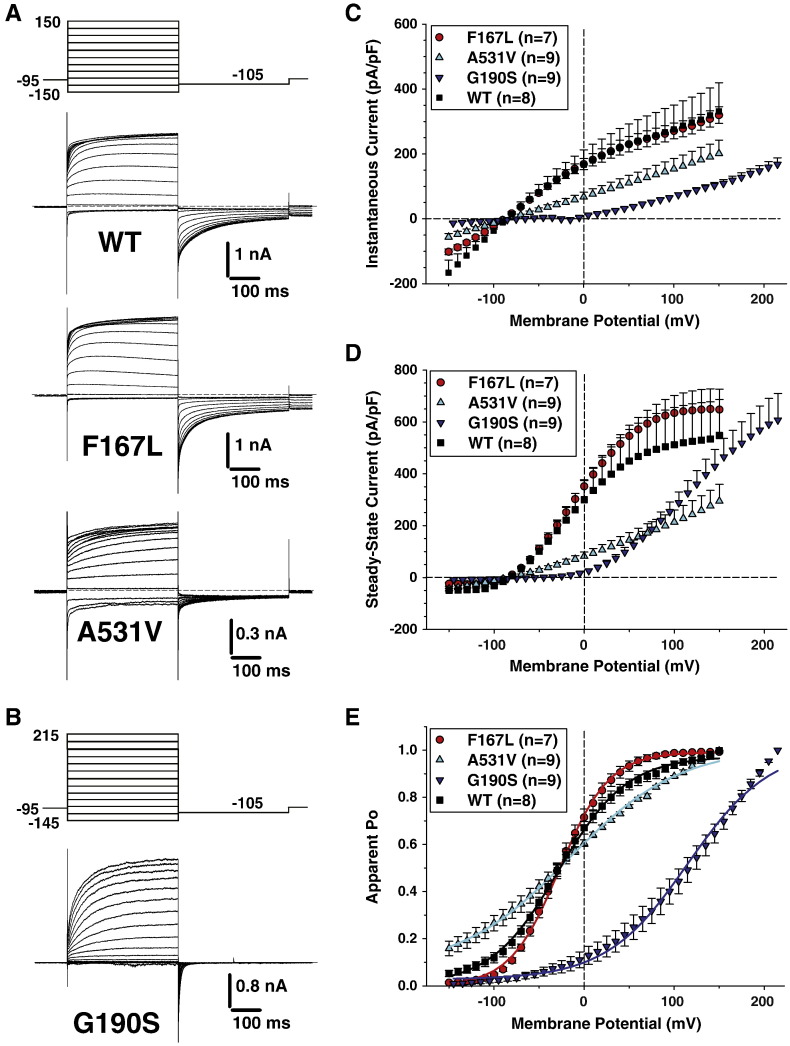
Fig. 2.
Voltage-dependence of wild-type and F167L, A531V, and G190S myotonic hClC-1 channels in low intracellular chloride. A) Chloride currents were recorded in HEK293 cells transfected with wild-type, F167L, or A531V hClC-1 variants. Cells were held at − 95 mV and 400 ms voltage pulses were applied from − 150 to + 150 mV in 10-mV intervals every 3 s. For clarity only current traces obtained every 20 mV are shown. Chloride currents displayed similar kinetics, but A531V had reduced amplitude. B) Voltage pulses were applied from − 145 to + 215 mV to elicit chloride currents in HEK293 cells expressing G190S hClC-1 variant. C) The instantaneous current density–voltage relationships were obtained as in Figs. 1C. D) The steady-state current density–voltage relationships were drawn as in Figs. 1D. E) The voltage dependence of activation, determined as in Fig. 1D, were fit with a Boltzmann function (Eq. (1)). Fit parameters are reported in Table 1. The activation voltage dependences of WT, F167L, and A531V show little variation, whereas G190S channels displayed a positively-shifted voltage dependence.