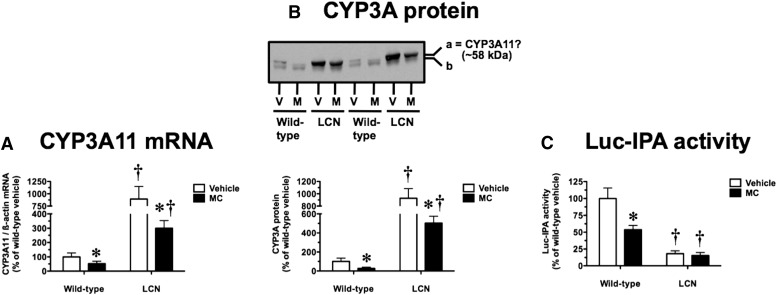
Fig. 1.
Effect of MC treatment on hepatic CYP3A11 mRNA (A), CYP3A protein immunoreactivity (B), and Luc-IPA catalytic activity (C) in WT and LCN mice. (B) Immunoblot of microsomal protein (5 µg) using polyclonal antibody against rat CYP3A2, showing results for two vehicle (V)–treated and MC (M)–treated mice per genotype. This antibody recognizes two mouse protein bands, as shown by the “a” and “b” labels on the right side, with the more prominent upper band “a” thought to represent CYP3A11. Quantitative analysis of CYP3A11 mRNA levels, relative to β-actin (A), CYP3A protein immunoreactivity levels as reflected by band “a” intensity (B), and Luc-IPA activity (C). Data represent the mean ± S.D. of determinations from four mice per group, expressed as a percentage of the mean for the vehicle-treated WT mice. The P values for the two-way ANOVA main effects for the Luc-IPA data were P = 0.0001 (treatment), P < 0.0001 (genotype), and P = 0.0004 (interaction). Outcomes from nonparametric Welch-corrected unpaired t tests (CYP3A11 mRNA and CYP3A protein immunoreactivity, where heterogeneity of variance was detected) and Bonferroni-corrected post tests (Luc-IPA activity) were as follows: *significantly different (P < 0.05) from genotype-matched vehicle-control mice; †significantly different (P < 0.05) from treatment-matched WT mice.