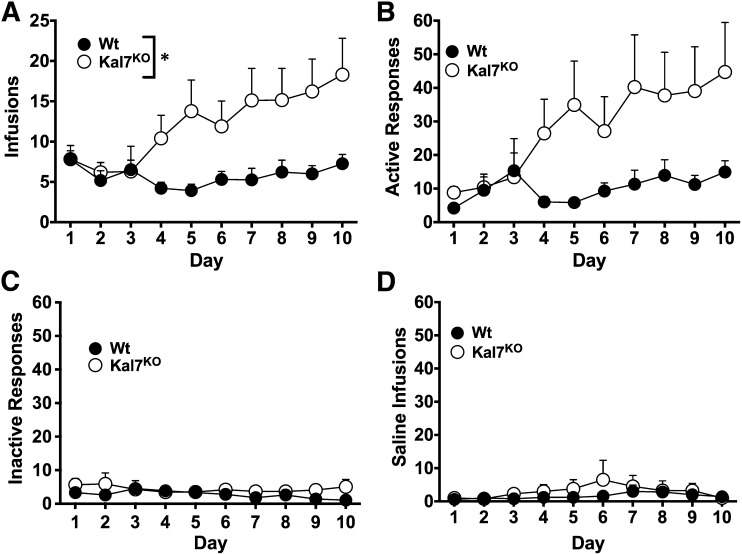
Fig. 2.
Cocaine self-administration at 0.5 mg/kg/infusion and saline. (A) When given daily training on an FR1 schedule for cocaine infusions, male Kal7KO mice earned a significantly higher level of infusions than their Wt littermates (repeated-measures two-way ANOVA: genotype F(1,48) = 5.34, *P = 0.025) with additional main effects of day (F(9,432) = 2.7, P = 0.005) and a significant genotype x time interaction (F(9,432) = 2.69, P = 0.005). (B) The pattern of responding on the active aperture (active responses) was similar to that seen with infusions, with a main effect of day (F(9,342) = 3.65, P < 0.001), but no significant effect of genotype was observed due to increased variability (F(1,38)=2.96, P = 0.09). Both Wt and Kal7KO mice exhibited low levels of responding for both the inactive aperture (C) and for infusions of saline (D), with no statistically significant differences by repeated-measures two-way ANOVA on either measure (P ≥ 0.19 for all). A total of 50 animals received cocaine (Wt, N = 23; Kal7KO, N = 27) and 10 received saline (Wt, N = 5; Kal7KO, N = 5).