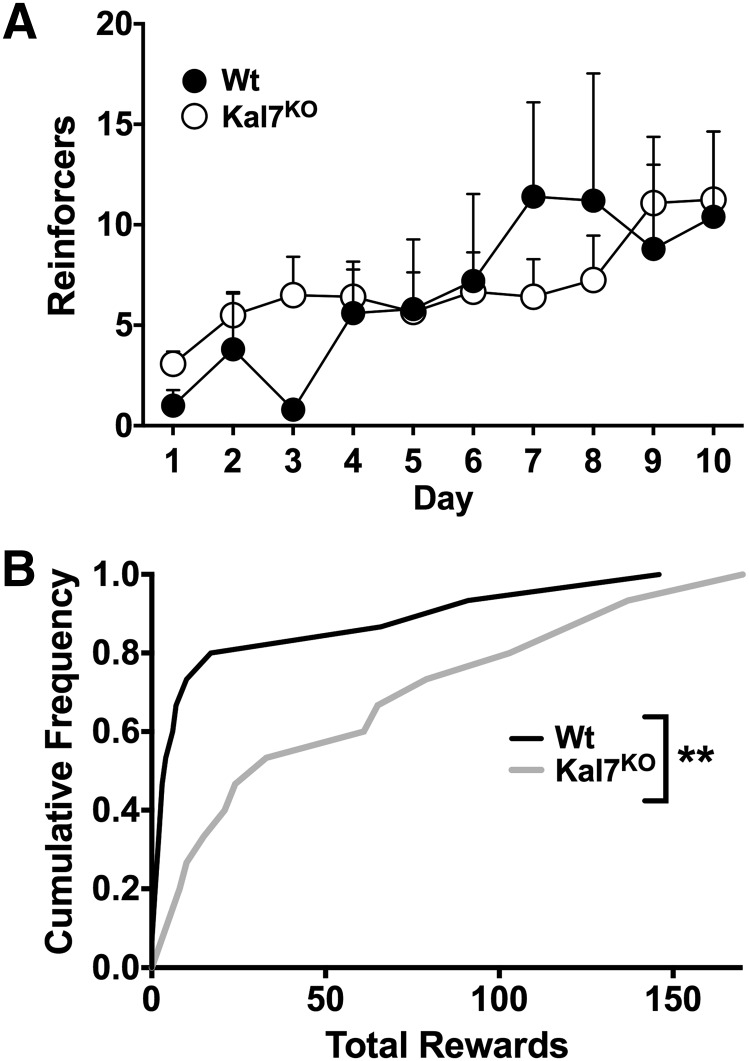
Fig. 5.
Instrumental responding for food. Cocaine-naïve animals that were food restricted for 5 days (Wt, N = 5; Kal7KO, N = 12) were then tested for operant responding for a grain pellet reward on an FR1 schedule for 10 days. When the number of reinforcers earned is examined by day (A), there are no differences in responding by genotype (repeated-measures two-way ANOVA: F(1,15) = 0.02; P = 0.90). There is a significant increase in responding across days (F(9,135) = 3.51; P < 0.001) but no genotype by day interaction (F(9,135) = 0.99; P = 0.45). (B) Plot of the total number of reinforcers earned by each animal as a cumulative distribution plot shows a strong right shift of the Kal7KO curve, indicating that a larger segment of the Kal7KO population garners a greater number of food rewards over time. Additionally, the large population of low responders (Wt, N = 15; Kal7KO, N = 15) excluded from the analysis in A is evident from the course of the Wt line. These results are significant based on Kolmogorov-Smirnov analysis (**P = 0.002).