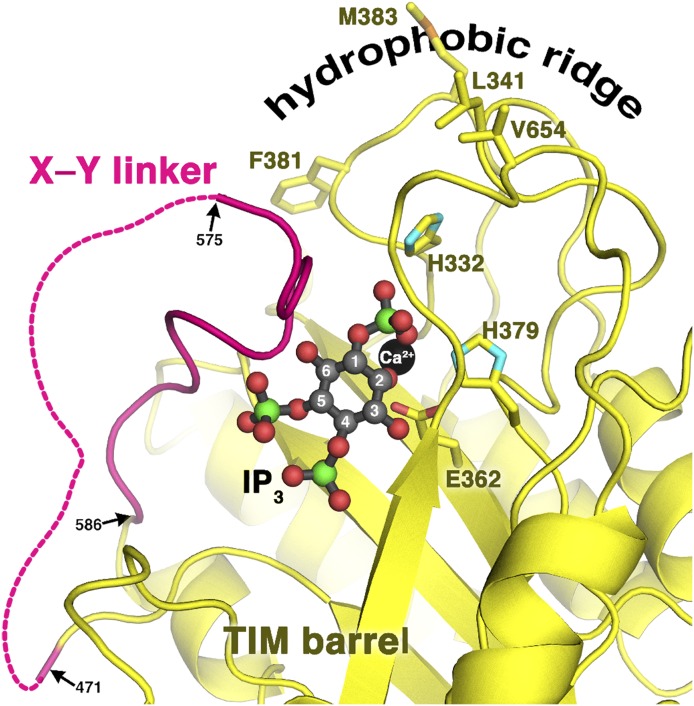
Fig. 3.
The PLCβ X–Y linker blocks the active site. A model of IP3 (derived from PDB ID 1DJX) bound to the PLCβ3 active site reveals a possible mechanism for autoinhibition by the X–Y linker. As observed in six independent structures of PLCβ enzymes, the ordered region of the X–Y linker (PLCβ3 residues 575–586) docks in a position that would prevent PIP2 from entering the enzyme active site. Displacement of this region of the X–Y linker would therefore appear to be a prerequisite for PIP2 binding. The catalytic residues H332, H379, and E362 are shown as sticks, and the active site Ca2+ as a black sphere. Dashed lines indicate the disordered region of the PLCβ3 linker, which contains a span of acidic residues. Side chains of residues that constitute the hydrophobic ridge, which is thought to help anchor the catalytic core to the membrane, are also shown.