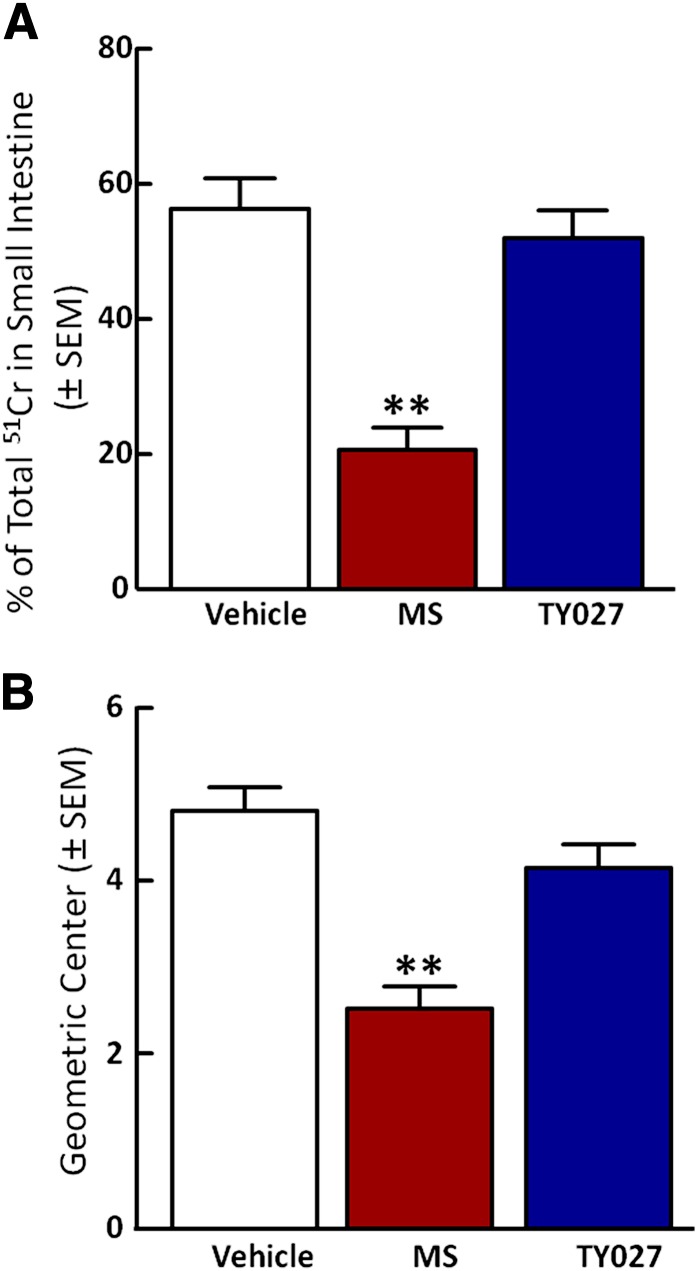
Fig. 6.
TY027 does not impair gastrointestinal transit in mice. Gastrointestinal transit was evaluated in mice after intravenous administration of either vehicle, MS, or TY027 by measuring gastric emptying of stomach gavaged 51Cr into the intestine (A) and calculating the geometric center to determine the distance of propulsion (B). MS (1 mg/kg i.v.; n = 8) significantly slowed emptying and reduced the geometric center compared with vehicle, whereas TY027 (3 mg/kg i.v.; n = 8) did not significantly decrease gastric emptying nor reduce the distance of 51Cr propulsion. Data represent the mean ± S.E.M. **P ≤ 0.001.