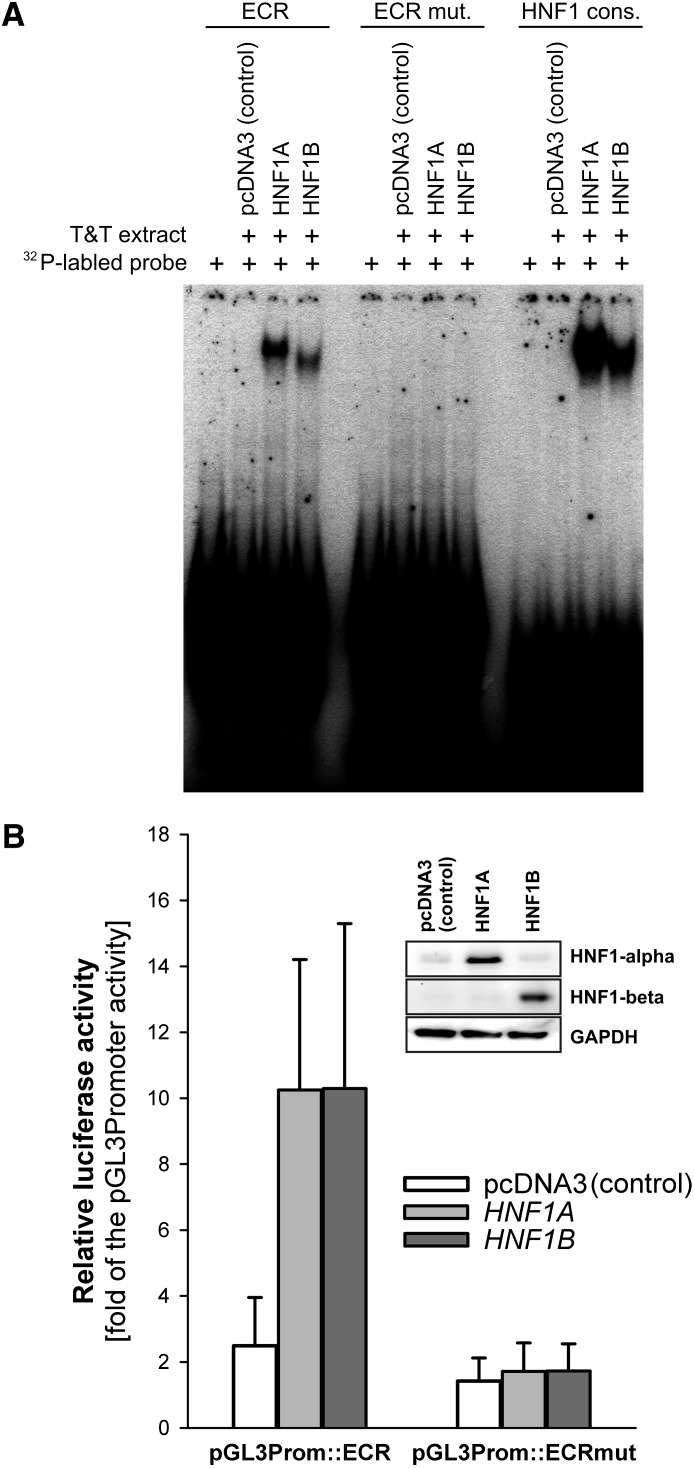
Fig. 5.
Comparison of the ability of HNF1α and HNF1β isoforms to interact with the intron 1 ECR and to regulate OCT1 promoter activity. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays of in vitro transcribed and translated HNF1α and β. pcDNA3 expression vectors carrying the HNF1A or HNF1B genes, or the empty pcDNA3 vector as a control, were in vitro transcribed and translated using the TNT T7 Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation System (Promega). The in vitro extracts were incubated with 32P-labeled probes containing the 40-bp conserved region from the ECR (ECR), the conserved region with both HNF1 binding sites mutated (ECR mut.), or a consensus binding sequence for HNF1 (HNF1 cons.) (Jain et al., 2007). (B) Luciferase reporter gene assay of Huh7 cells overexpressing the HNF1α or HNF1β isoforms. The overexpression vectors were cotransfected with pGL3 promoter vectors carrying the luciferase reporter gene under the control of the Simian virus 40 promoter and the intact or mutated intron 1 ECR (pGL3Prom::ECR and pGL3Prom::ECR mut., respectively). Shown are means and standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. The overexpression of HNF1α and HNF1β was confirmed by Western blot.