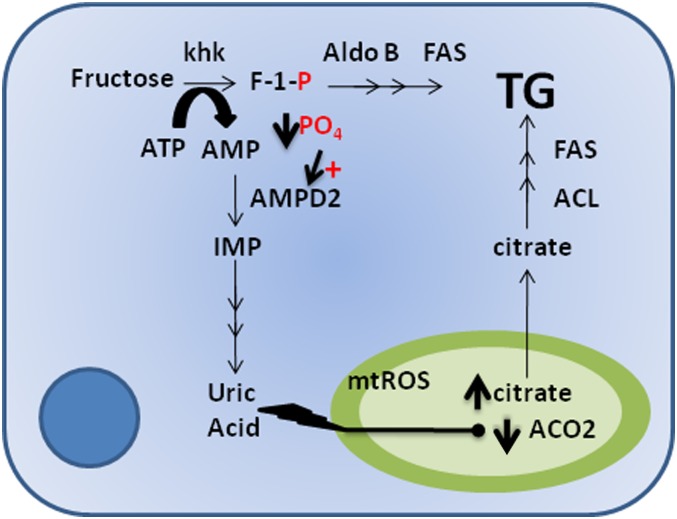
FIG. 2.
Classic and alternative lipogenic pathways of fructose. In the classical pathway, triglycerides (TG) are a direct product of fructose metabolism by the action of multiple enzymes including aldolase B (Aldo B) and fatty acid synthase (FAS). An alternative mechanism was recently shown (30). Uric acid produced from the nucleotide turnover that occurs during the phosphorylation of fructose to fructose-1-phosphate (F-1-P) results in the generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress (mtROS), which causes a decrease in the activity of aconitase (ACO2) in the Krebs cycle. As a consequence, the ACO2 substrate, citrate, accumulates and is released to the cytosol where it acts as substrate for TG synthesis through the activation of ATP citrate lyase (ACL) and fatty acid synthase. AMPD2, AMP deaminase 2; IMP, inosine monophosphate; PO4, phosphate.