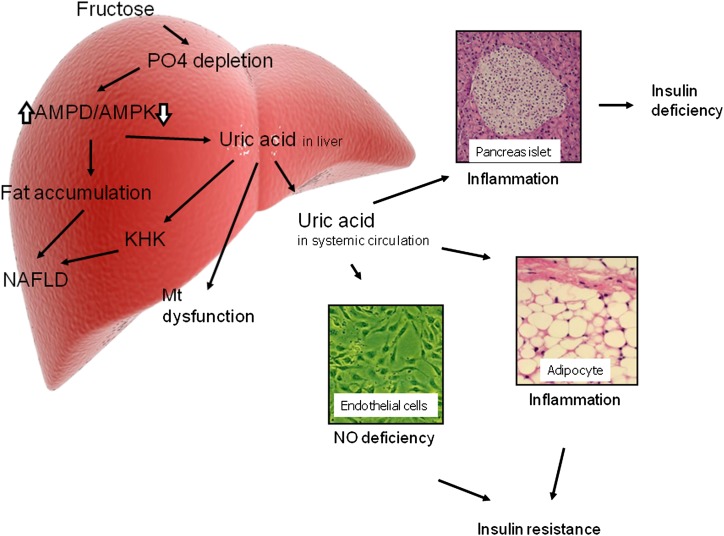
FIG. 3.
Uric acid: potential mechanisms for insulin resistance and diabetes. Uric acid may contribute to insulin resistance in the liver by inducing mitochondrial oxidative stress and steatosis (28). Uric acid also blocks the ability of insulin to stimulate vasodilation of blood vessels, which is important for the delivery of glucose to the skeletal muscle (4,32). Uric acid also induces local inflammation in the adipose tissue with a reduction in the production of adiponectin (44). Finally, uric acid may also have direct effects on the islet cells leading to local oxidative stress and islet dysfunction (5). Mt, mitochondria; PO4, phosphate.