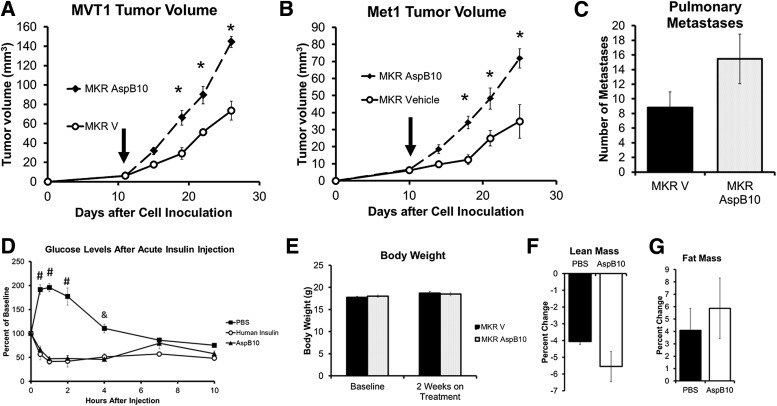
FIG. 3.
Chronic activation of the IR by the insulin analog AspB10 increased orthotopic Met1 and MVT1 tumor growth. MKR mice were injected with MVT1 or Met1 tumor cells on Day 0. Treatment was started with AspB10 (12.5 IU/kg, twice daily s.c.) or vehicle, indicated by vertical arrow (A and B). AspB10 led to increased growth of both MVT1 and Met1 tumors (A and B). The number of pulmonary macrometastases showed a nonsignificant increase in the AspB10-treated group (C). An insulin tolerance test was performed with AspB10 (12.5 IU/kg s.c.), regular human insulin (12.5 IU/kg s.c.), and PBS (vehicle). Blood glucose was measured at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 7, and 10 h after injection (D). Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA for comparing more than two groups: #P < 0.05 between PBS and AspB10 and human insulin groups; &P < 0.05 between PBS- and AspB10-treated groups; n = 4 per group. #PBS group was significantly greater than other groups, P < 0.05; &PBS group was significantly higher than AspB10 group, P < 0.05. No change in body weight (E) or difference in relative lean or fat mass (F and G) was observed after 2 weeks of AspB10 administration. Graphs are representative of two studies. All graphs show the mean for each group, and error bars represent the SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed t test. *P < 0.05 between groups. n = 9–11 mice per group. MKR V, MKR mice with endogenous hyperinsulinemia.