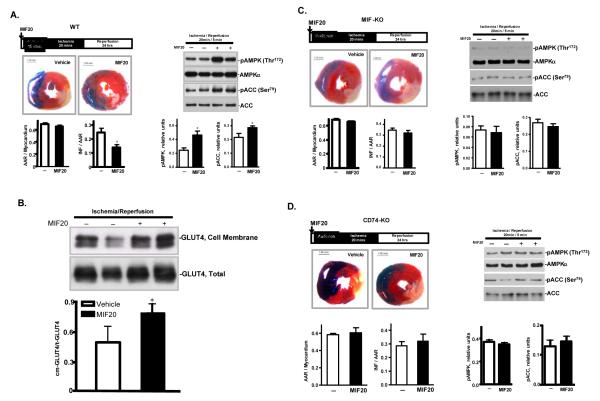
Figure 7.
MIF20 reduces myocardial necrosis and activates AMPK in mouse heart in vivo in a MIF and MIF receptor dependent fashion. Anesthetized mice were subjected to 20 min regional ischemia by ligation of the left coronary artery followed by 24 hours of reperfusion. MIF20 or vehicle was injected intra-peritoneally 15 min prior to ischemia. (A) Representative pictures show myocardial infarct size in heart sections defined by dual staining with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium (TTC) and Evans Blue. Bar graphs quantify the ratio of the area at risk (AAR) to myocardium, and the ratio of infarct size (INF) to AAR. AMPK and ACC phosphorylation in different tme periods during ischemia and reperfusion was assessed by western blotting. (B) MIF20 treatment is associated with enhanced GLUT4 translocation to the membrane of myocardial tissue. (C) Lack of MIF20 effect on myocardial necrosis, AMPK and ACC phosphorylation in MIF-KO mice. (D) Lack of MIF20 effect on myocardial necrosis, AMPK and ACC phosphorylation in MIF receptor (CD74-KO) mice. n=4-6 hearts for each studied group. *p<0.05 vs. vehicle.