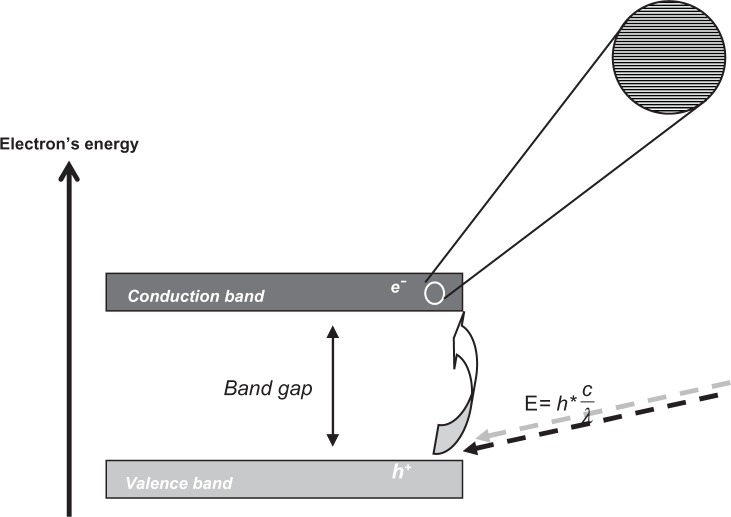
Figure 2.
Graphical representation of the band gap in a semiconducting material. The electronic structure of the semiconductor is characterized by bands that consist of orbitals. Bands are separated by gaps in the energy for which there are no orbitals. Upon light absorption of minimally the band gap energy, a valence band electron (e−) is excited to the conduction band leaving a hole in the valence band (h+).