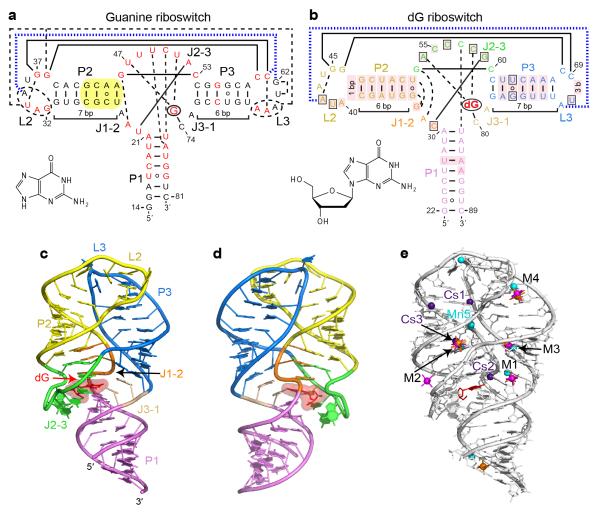
Figure 1.
Overall structure and tertiary interactions of the dG-bound M. florum riboswitch. a, Secondary structure and tertiary interactions in the Bacillus subtilis xpt G riboswitch15 (PDB ID 1Y27). Canonical and non-canonical tertiary base pairing is depicted by long solid and dashed lines, respectively. Tertiary stacking interactions are in thick dashed blue lines. Nucleotides in red correspond to the positions that are >90% conserved in the known guanine riboswitch representatives13. Note that some conserved positions preserve chemical signatures (purine or pyrimidine) rather than the identity of nucleotides. Yellow shading shows a helical region whose replacement by the corresponding segment of the dG riboswitch significantly enhances dG binding17. The bound ligand is circled and its chemical formula is shown in inset. b, Secondary structure and tertiary interactions in the dG riboswitch. Pink shading indicates nucleotide differences from the guanine riboswitch. Boxes depict nucleotide variations from the guanine riboswitch that occur at otherwise highly conserved positions. c, Overall riboswitch structure in a ribbon representation, front view. d, Same structure, back view. e, Summary of the metal binding sites located using anomalous scatterers. Cs+ (indicated Cs), Mn2+ (indicated Mn), [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Ir(NH3)6]3+ cations are shown in purple, cyan, orange and pink colors, respectively. General metal binding sites, where more than one cation type was detected, are designated M1 through M4.