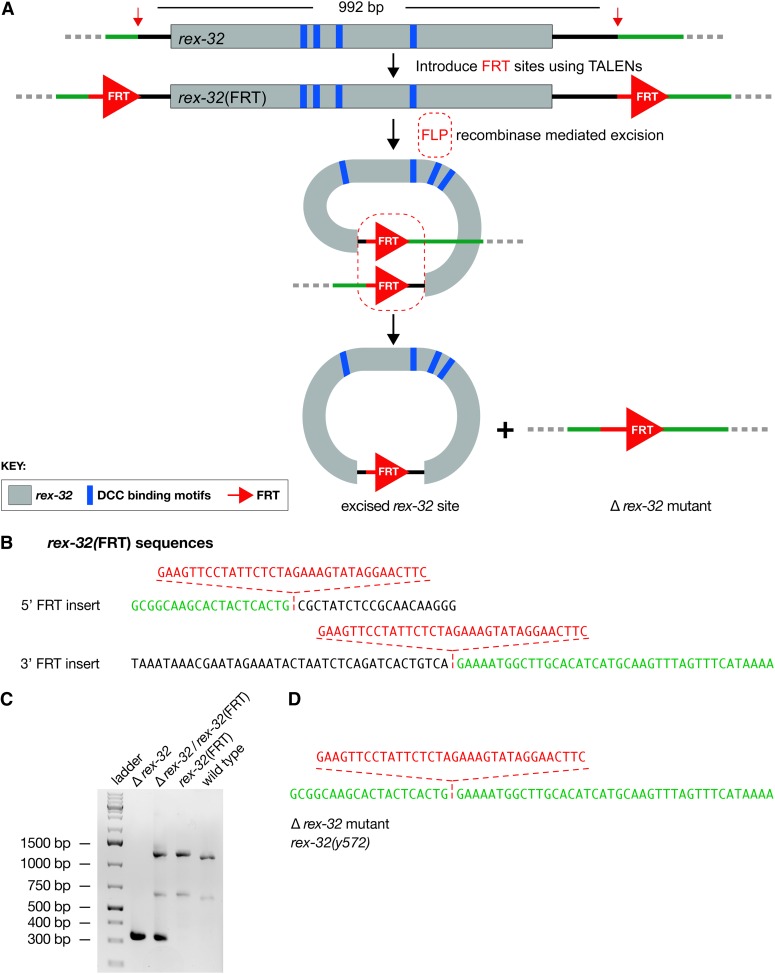
Figure 4.
FLP-FRT-mediated deletion of the rex-32 DCC binding site. (A) Diagram of rex-32 (gray) with its four DCC binding motifs (blue) and the scheme to delete it. FRT sites (red) were inserted at opposite ends of rex-32 via HDR, using the TALENs and ssOligos shown in Figure S3. RNA encoding FLP recombinase was introduced into the germline of the FRT-containing animals, and F2 animals were screened by PCR for the deletion events. (B) DNA sequences of regions carrying the 5′- and 3′-FRT insertions. They are identical to those of the ssOligos used to make the FRT insertions. (C) Agarose gel of PCR products from a homozygous rex-32 deletion strain (360 bp), a heterozygous strain bearing the rex-32 deletion in trans to the FRT-containing rex-32, a homozygous rex-32 FRT strain (1251 bp), and a wild-type strain (1183 bp). The PCR product from the wild-type strain is smaller because it lacks the FRT inserts. The gel verified the deletion, and (D) DNA sequence analysis confirmed that the deletion was precise.