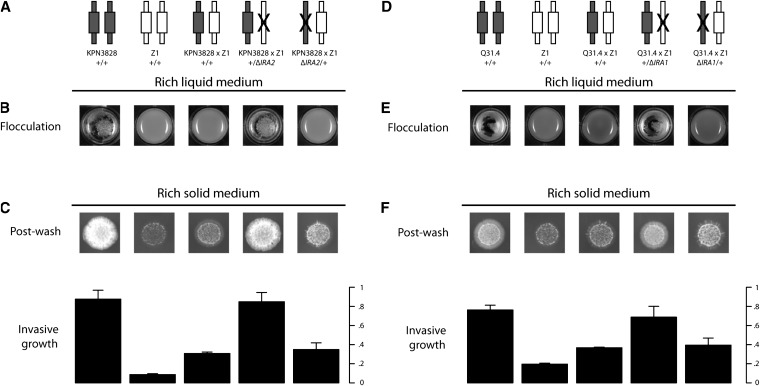
Figure 3.
Variation at IRA1 and IRA2 underlies flocculation and invasive growth. Each panel reports results of reciprocal hemizygote analysis of genetic variation at an IRA gene, between one flocculent, invasive European strain and the nonflocculent European strain Z1. Each column represents one strain, with each element in the bottom panels showing results from the strain indicated at top. (A and D) Each cartoon represents one diploid strain, with the haploid genome inherited from a flocculent parent or Z1 represented as a symbol with dark or light shading, respectively, and a solid X indicating an engineered loss-of-function of an IRA gene as indicated in labels. Δ, engineered loss-of-function allele. The fourth and fifth strains in each experiment are isogenic to one another at all loci except the IRA gene indicated, such that trait variation between them can be attributed to genetic differences at the manipulated IRA locus. (B and E) Overnight cultures in rich liquid medium as in Figure 1. (C and F) Invasive growth assays of colonies grown on solid medium as in Figure 1. Bar heights report mean invasive growth measurements of two replicate colonies and error bars represent one standard deviation.