Figure 7.
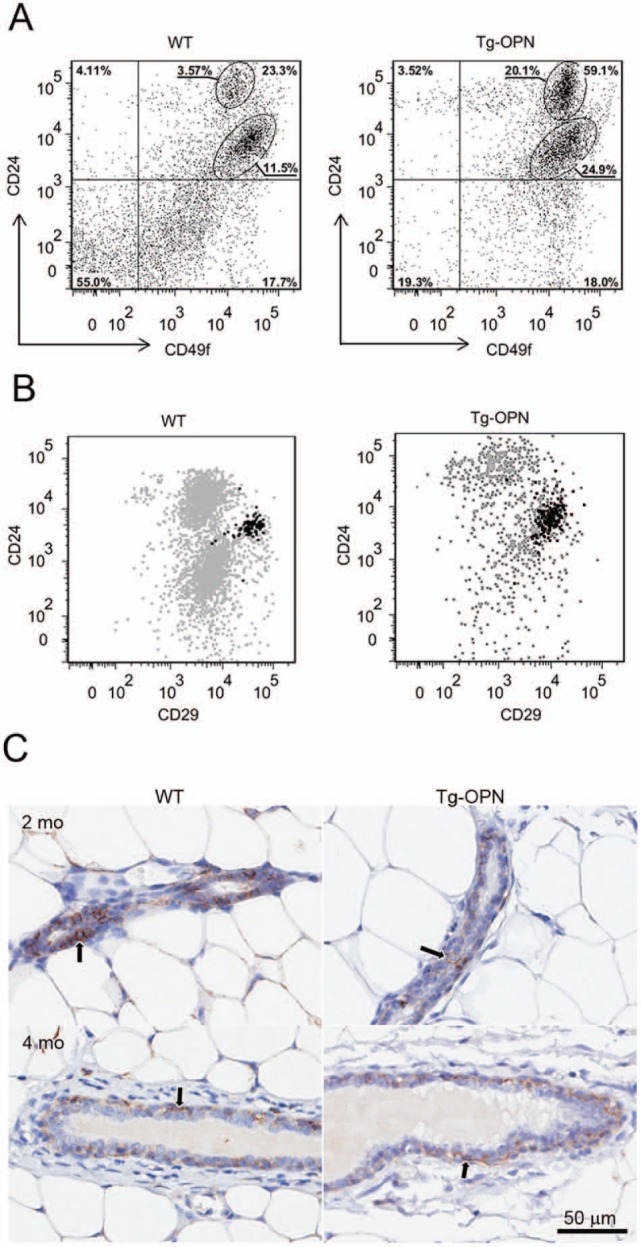
Expression of putative stem cell markers in wild type (WT) and transgenic osteopontin (Tg-OPN) mammary epithelial cells. The gating strategy used to select for CD49f+ cells is described in Supplemental Figure S2. Distribution of CD49f+ cells in Tg-OPN as well as in WT littermate control mammary epithelial cells according to their expression of the putative stem cell markers CD24 and CD29 (A). Representative dot plot showing the distribution of CD44+ cells among the CD49f+ CD24 and CD29 expressing cells (B). Anti-CD44 immunohistochemistry (C) on 2- and 4-month-old nulliparous mammary glands from WT and Tg-OPN animals shows that CD44+ cells (arrows) are located primarily in the basal compartment of ducts with fewer in the luminal compartment. The younger animals appear to have more CD44+ cells in the luminal compartment, and it appears that the Tg-OPN has fewer luminal CD44+ cells compared to the WT.
