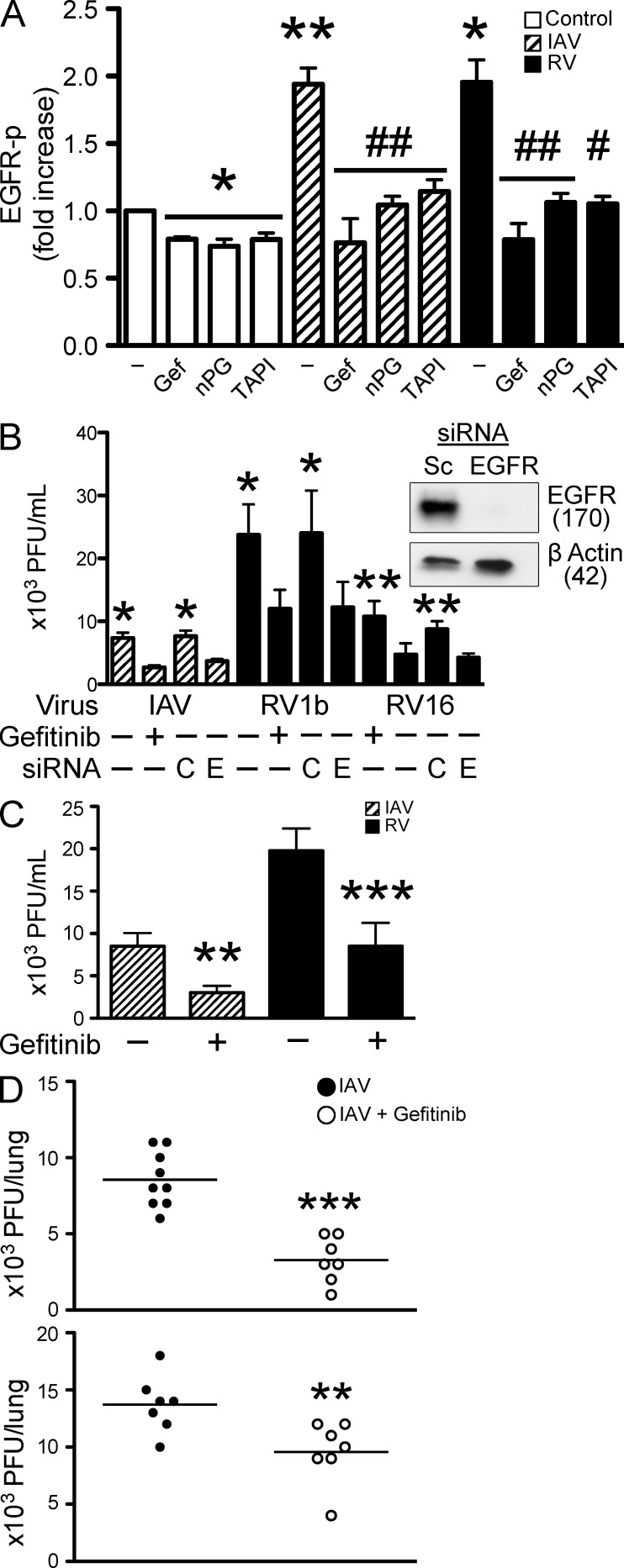
Figure 1.
Role of EGFR in respiratory viral infection. (A) EGFR-p was measured by ELISA at 10 min in BEAS-2b cell culture lysates. Cells were treated with serum-free medium alone (control), with the selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor 10 µM Gefitinib, ROS scavenger (nPG, 100 µM), MP inhibitor (TAPI, 10 µM), with IAV and RV1b alone, or with the addition of nPG and TAPI (n = 3–5 independent experiments, mean ± SEM; *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.005 vs. control; #, P < 0.01 and ##, P < 0.005 vs. each virus alone). (B) BEAS-2b cells were treated with IAV, RV1b, and RV16 alone, with 10 µM Gefitinib alone, or transfected with control (C) or EGFR siRNA (E). After 24 h, cell culture homogenates were collected and virus was quantified by plaque assay (n = 3–4 independent experiments, mean ± SEM; *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01 vs. virus plus Gefitinib or EGFR siRNA). BEAS-2b cells were transfected with EGFR siRNA and EGFR protein was assessed by Western blot (representative of three independent experiments). Molecular masses are provided in kilodaltons. (C) NHBE cells were treated with IAV and RV16 alone, or with 10 µM Gefitinib for 24 h and viral titers in cell culture homogenates were quantified by plaque assay (n = 4 independent experiments, mean ± SEM; **, P < 0.005 and ***, P < 0.0001 vs. virus alone). (D) C57BL/6 mice were infected (intranasal) with IAV (104.5 TCID50%) alone, or with 50 mg/kg Gefitinib and viral titers were quantified by plaque assay at 48 h. In a prophylaxis model (top), Gefitinib was given 16 h before viral infection and then continued daily, and in a therapeutic model (bottom), Gefitinib was given 1 h after viral infection and then continued daily (n = 7–9 mice/group repeated twice, mean ± SEM; **, P < 0.01 and ***, P < 0.001 vs. virus alone).