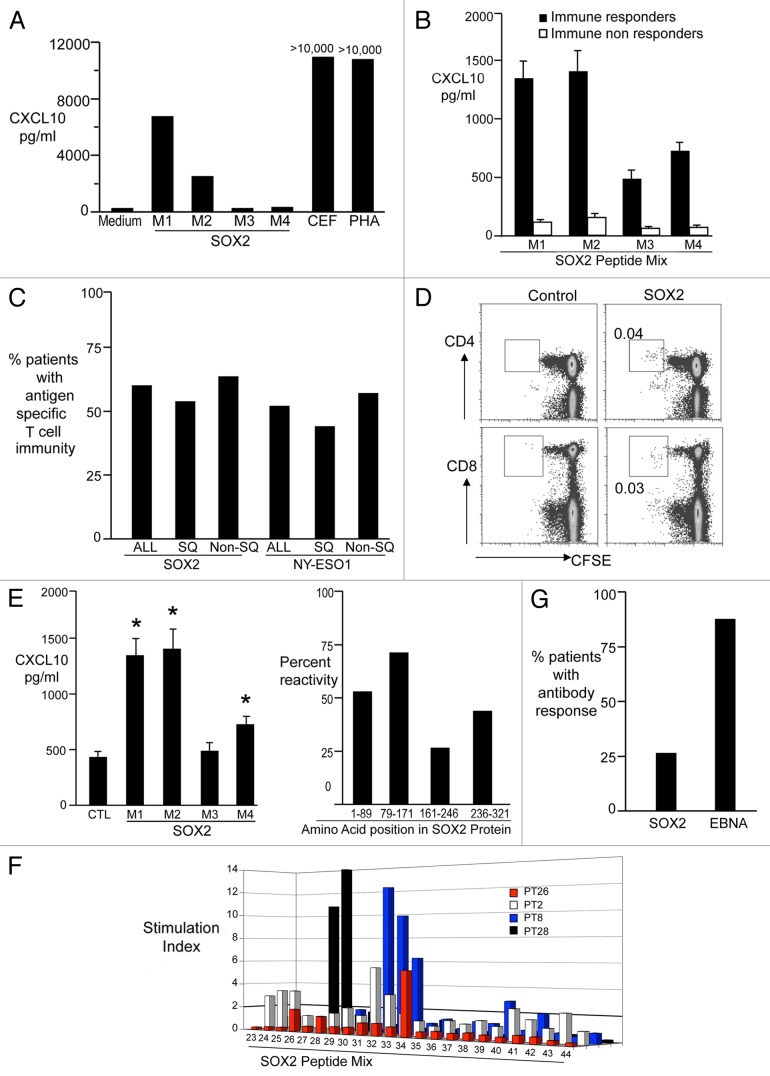
Figure 2. Detection of antigen-specific cellular and humoral responses in non-small cell lung carcinoma patients. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were co cultured with medium alone, overlapping peptides from the SOX2 library (3 μg/ml, M1 M2 M3 M4), CEF peptides or phytohemagglutinin (PHA). After 48 h, supernatants were harvested and examined for the abundance of CXCL10. M1 peptides cover SOX2 residues 1–89, M2 residues 79–171, M3 residues 161–246 and M4 residues 236–321. See also Table S2. (A) Representative results from a patient exhibiting SOX2-reactive T cells. (B) CXCL10 production (mean ± SEM) in response to SOX2 antigens (M1–4) for patients classified as immune responders (n = 15) vs. non-responders (n = 9). (C) PBMCs obtained from patients with advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) were tested for the presence of T cells reacting against SOX2 (n = 35) or NY-ESO-1 (n = 23) using overlapping peptides as in Figure 2A and B. The percentage of all NSCLC patients (ALL), squamous NSCLC patients (SQ) and non-squamous (Non-SQ) NSCLC patients exhibiting immunity to SOX2 (ALL = 60%) or NY-ESO-1 (ALL = 52%) is reported. (D) PBMCs from lung cancer patients were labeled with CFSE and co-cultured with peptides from the SOX2 library (5 μg/mL) in the presence of anti-CD28 and anti-CD49d (both at 1 μm/mL) for 7 d. Eventually, T-cell proliferation was determined using flow cytometry. (E) Reactivity of T cells from SOX2-immune patients to the different regions of the SOX2 protein. Both the amount of CXCL10 (mean ± SEM; left panel) and the % samples reacting to individual mixes are reported. *p < 0.05 compared with control. Please note PBMCs from some patients reacted against more than one region of SOX2. (F) Fine mapping of SOX2 reactivity. PBMCs were incubated with individual peptides from the SOX2 library for 48 h and tested for the presence of CXCL10 using a luminex assay. Figure shows individual peptide reactivity in PBMCs from 4 different patients. (G) Detection of anti-SOX2 antibodies. Plasma obtained from patients was tested for the presence of antibodies specific for SOX2 and EBV nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) by ELISA. The percentage of patients with bearing antibodies against SOX2 (28%) and EBNA1 (88%) detectable at a titer of > 1:100 is reported.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.