Figure 2.
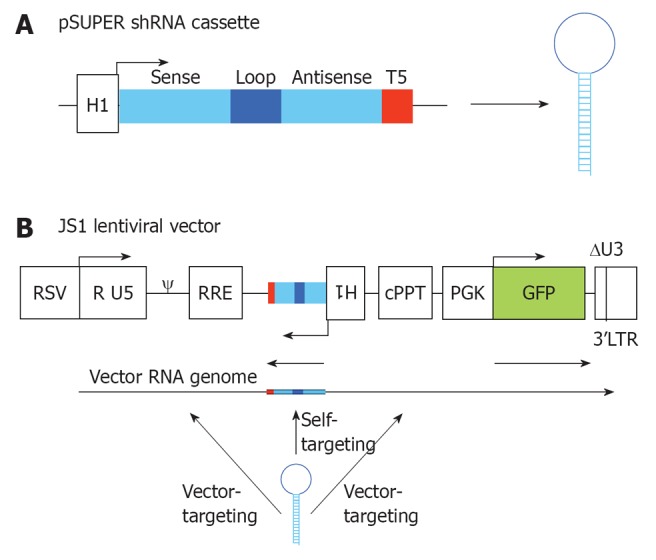
RNA interference vector constructs. A: Two complementary DNA oligonucleotides are annealed and cloned into pSUPER downstream of the H1 promoter that triggers short hairpin RNA (shRNA) expression. The shRNA cassette encodes a 19 nt sense strand, 9 nt loop, 19 nt antisense strand and a stretch of 5 T’s (T5), which is the termination signal; B: The shRNA cassette was cloned in the lentiviral vector JS1 for stable transduction of human T cells. The shRNA cassette is cloned in antisense direction to avoid promoter interference. During vector production three transcripts are produced from the lentiviral vector: the shRNA, the vector RNA genome and the GFP transcript. The shRNA will have a 100% target match with the shRNA-encoding sequence in the vector RNA genome (self-targeting), and potential targets in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) derived sequences of the lentiviral vector (vector-targeting). RSV: Respiratorial syncytial virus promoter; R U5: R and U5 element of HIV-1 promoter; ψ: Packaging signal; RRE: Rev responsive element; cPPT: Central polypurine tract; PGK GFP: Green fluorescent protein driven from a PGK promoter; 3’LTR: 3’ long terminal repeat of HIV-1, with deletion in the U3 region.
