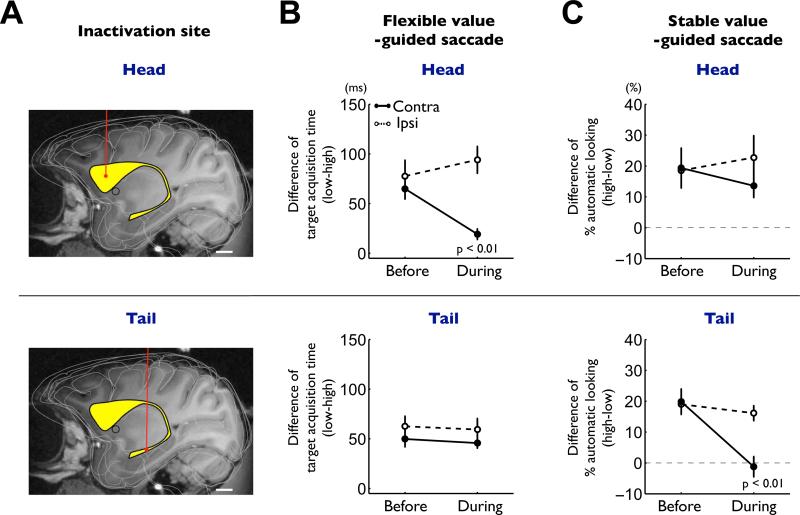
Figure 8. Differential impairments of flexible and stable value-guided saccades by caudate head and tail inactivations.
(A) Example injection sites of muscimol in the caudate nucleus (yellow structure) reconstructed on an MR image: caudate head (top) and tail (bottom). Scale bar indicates 5 mm. (B) Effects on the controlled saccades in the flexible value procedure (Figure 1B). The differences in the target acquisition time between high- and low-valued objects are plotted before and during inactivation (mean ± SE). Data are shown separately for caudate head inactivation (top, n = 6) and tail inactivation (bottom, n = 9), and for contralateral saccades (solid line) and ipsilateral saccades (dashed line). (C) Effects on the automatic saccades in the stable value procedure (free-looking task, Figure 1D). The differences in the probability of automatic looking between high- and low-valued objects are plotted before and during inactivation (mean ± SE). Same format as in (B). See also figure S6-8.