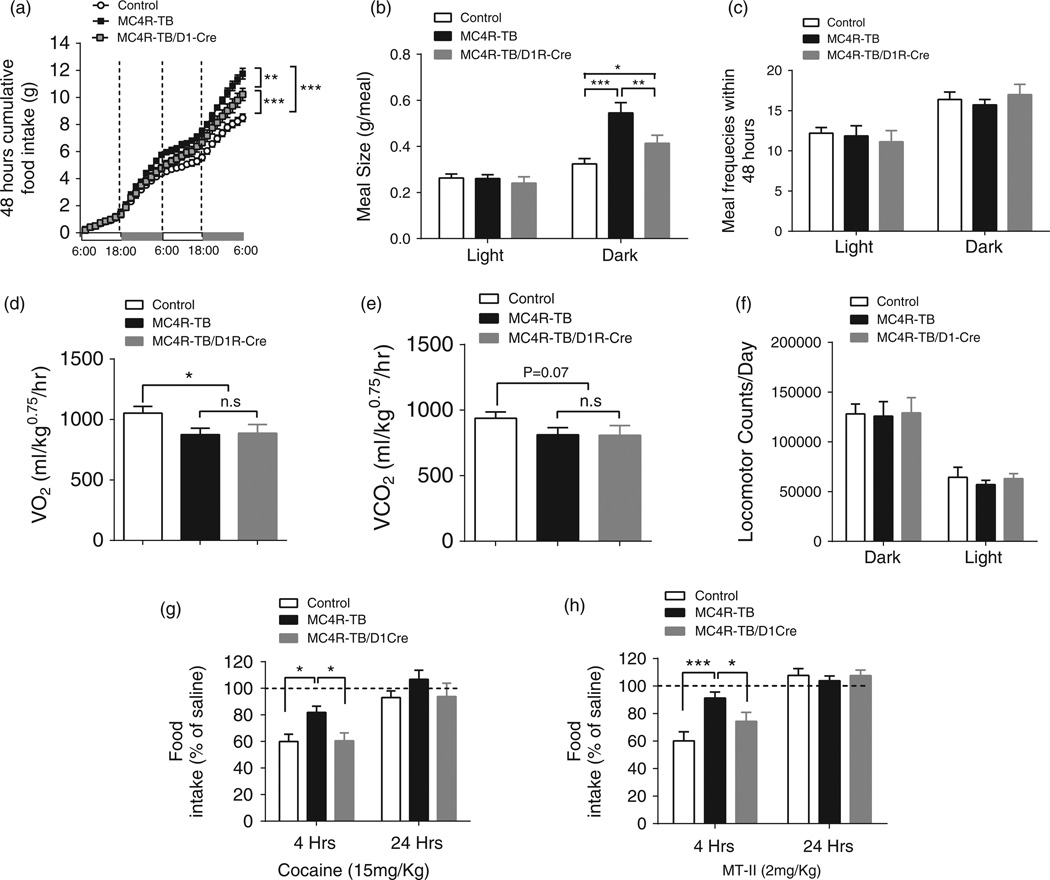
Figure 2. MC4R signaling in D1R neurons regulates meal size and acute cocaine-induced anorexia.
(a–f) Metabolic cage analysis confirmed reduction of food intake in MC4R/D1R mice (a) and further showed that restoration of MC4Rs in D1R neurons reduces meal size (b), but not meal frequency (c), in the dark cycle. Oxygen consumption (d), carbon dioxide production (e) and daily locomotor activity (f) were not affected in MC4R–TB/D1R mice. (g and h) Acute (g) cocaine- and (h) MTII-induced suppression of 4-h food intake was significantly blocked in MC4R–TB mice but normalized in MC4R/D1R mice. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared between the groups by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Data are presented as mean±SEM.