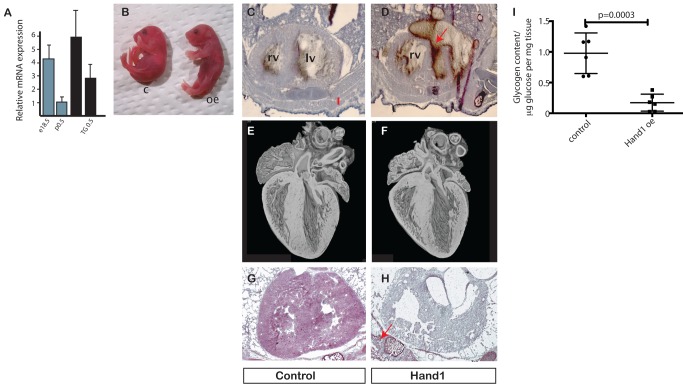
Figure 2. Prevention of neonatal Hand1 down-regulation in transgenic mouse hearts leads to cardiomyopathy and death.
(A) Cardiac RNA levels of Hand1 in e18.5 and p0.5 wild-type, and e18.5 and p0.5 transgenic (TG 18.5 and TG0.5, respectively) showing RNA levels in the transgenic heart around 2.5 times that of wild-type p0.5 heart. (B) Cardiac Hand1 elevating pups appear grossly normal, but are cyanosed (c, control; oe, Hand1 overexpressing). (C, D) H and E stain of cryostat section through thorax of control and Hand1 overexpressing hearts, showing thin ventricular wall of the Hand1 overexpressing heart, and ventricular rupture (arrowed) with blood in the pericardial space (rv, right ventricle; lv, left ventricle). (E, F) EFIC sectioning and reconstruction of control and Hand1 overexpressing hearts from 4-h-old fostered pups, showing small size but no gross structural defect. (G, H) Periodic acid-Schiff stain of control and Hand1 overexpressing heart, showing decreased glycogen levels in Hand1 overexpressing heart (purple). Glycogen stain in intercostal muscle of transgenic pup arrowed in (H). (I) Quantification of glucose enzymatically released from glycogen in hearts of neonates 2 h after caesarian section. Levels of glycogen in XMLC-Hand1 hearts are 17.5% of XMLC controls (p value, two-tailed t test, n = 6 hearts each group).