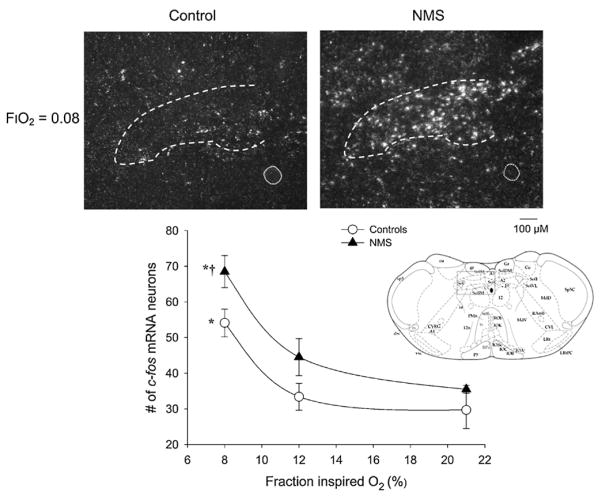
Fig. 6.
Neonatal maternal separation (NMS) augments c-fos m-RNA expression levels in the caudal NTS of awake rats following exposure to one of three fraction of inspired O2 level (FiO2 ) for 20 min: normoxia (FiO2 = 0.21), moderate hypoxia (FiO2 = 0.12), or severe hypoxia (FiO2 = 0.21). Top panels: representative photomicrographs comparing c-fos m-RNA in situ hybridization signal after exposure to severe hypoxia between control rats (left) and rats subjected to neonatal maternal separation (NMS; right). The dotted circle represents the central canal. Lower panel: relationship between the number of c-fos mRNA positive neurons within the NTS, and inspired O2 level for controls (open circles) and NMS rats (closed triangles) in the caudal NTS. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Each value represents the mean number of c-fos mRNA-containing perikarya were counted bilaterally from sections corresponding to the rostro-caudal coordinates −14.3 to −14.60 from bregma for each experimental condition. For each rat, a mean number of c-fos positive neurons was obtained by averaging perikarya counted for several sections (the number of sections ranged between 1 and 3). * indicates means that are statistically different from baseline value at p < 0.05. † indicates means that are statistically different from corresponding control value at p < 0.05.
Adapted with permission from Kinkead et al. (2008).