Table 2. Statistical correlation matrix results between variable pairs.
| Anatomical Symmetry | Dynamical Symmetry | Economy | ||||||||
| r max (PD) | r max (UD) | r max (LD) |

|
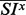
|
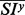
|
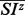
|
GI | C | ||
| Anatomical Sym. | r max (PD) | 1 | 0.501*; 0.040 | 0.427;0.087 | 0.871**; 0.000 | 0.651**; 0.005 | 0.110;0.675 | −0.094;0.719 | 0.606**; 0.010 | 0.157;0.547 |
| r max (UD) | 1 | 0.507*; 0.038 | 0.782**; 0.000 | 0.322;0.208 | 0.003;0.990 | 0.020;0.940 | 0.357;0.160 | −0.114;0.662 | ||
| r max (LD) | 1 | 0.748**; 0.001 | 0.045;0.863 | 0.103;0.694 | 0.304;0.236 | 0.046;0.860 | 0.059;0.822 | |||
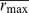
|
1 | 0.487*; 0.048 | 0.095;0.716 | 0.055;0.834 | 0.473;0.055 | 0.072;0.785 | ||||
| Dynamical Sym. |
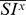
|
1 | 0.186;0.447 | 0.009;0.972 | 0.992**; 0.000 | 0.005;0.983 | ||||
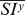
|
1 | 0.617**; 0.005 | 0.186;0.445 | 0.105;0.668 | ||||||
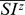
|
1 | 0.012;0.959 | 0.211;0.385 | |||||||
| GI | 1 | −0.001;0.995 | ||||||||
| Economy | C | 1 | ||||||||
Pearson Correlation coefficient is presented together with the relative p-value for the following parameters: maximal cross correlation values for each anatomical district (r
max(PD), r
max(UD) and r
max(LD)), global anatomical cross correlation value (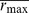 ), dynamical symmetry indices for each direction (
), dynamical symmetry indices for each direction (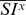 ,
,
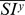 and
and 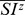 ), Global Symmetry Index (GI) averaged among the different running speeds for each subject and metabolic Cost of transport (C). Values in bold indicate significant correlations (* = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01).
), Global Symmetry Index (GI) averaged among the different running speeds for each subject and metabolic Cost of transport (C). Values in bold indicate significant correlations (* = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01).
