Figure 3.
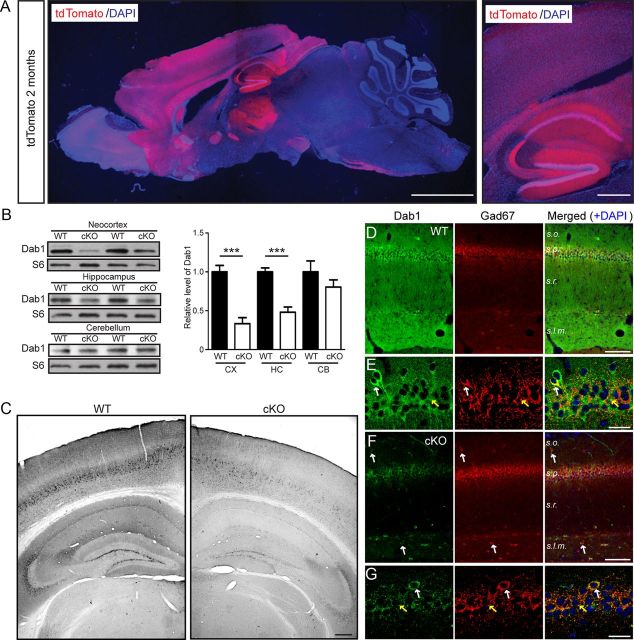
Adult forebrain excitatory neuron-specific loss of Dab1 expression in cKO mice. A, A representative brain section obtained from a 2-month-old cKO mouse also expressing the tdTomato reporter gene. The low-magnification example on the left shows predominant reporter gene expression in the forebrain, whereas the higher magnification example on the right shows elevated activity in the cerebral cortex, hippocampal area CA1, and dentate gyrus. Scale bars: left, 2 mm; right, 200 μm. B, Western blot analysis of Dab1 in brain regions of 2-month-old WT and Dab1 cKO mice. Blots were reprobed with antibodies against ribosomal protein S6 as a loading control. The data were quantified from n = 4–5 mice/genotype. Dab1 levels were significantly reduced in the cortex (CX) and hippocampus (HC), but not in the cerebellum (CB), of cKO mice compared with WT mice. Bar graphs indicate the mean ± SEM; ***p < 0.001. C, Immunoperoxidase staining of Dab1 in 2-month-old WT and cKO brains revealed widespread loss of Dab1 expression throughout the cortex and hippocampus. Scale bar, 200 μm. D, E, Double immunofluorescence of adult WT hippocampal sections stained with Dab1 (green) and GAD67 (red) antibodies. Magnified examples in E show that Dab1 is expressed mostly in the cell bodies of excitatory neurons, which are surrounded by inhibitory terminals (yellow arrows). Occasionally, colabeling of interneuron cell bodies was noted (white arrows). F, G, Double immunofluorescence of similar cKO sections reveals the specific loss of Dab1 in excitatory, pyramidal neurons, which unmasks the residual expression of Dab1 in the interneuron cell bodies (white arrows) and terminals (yellow arrows). Scale bars, D, F, 50 μm; E, G, 25 μm.