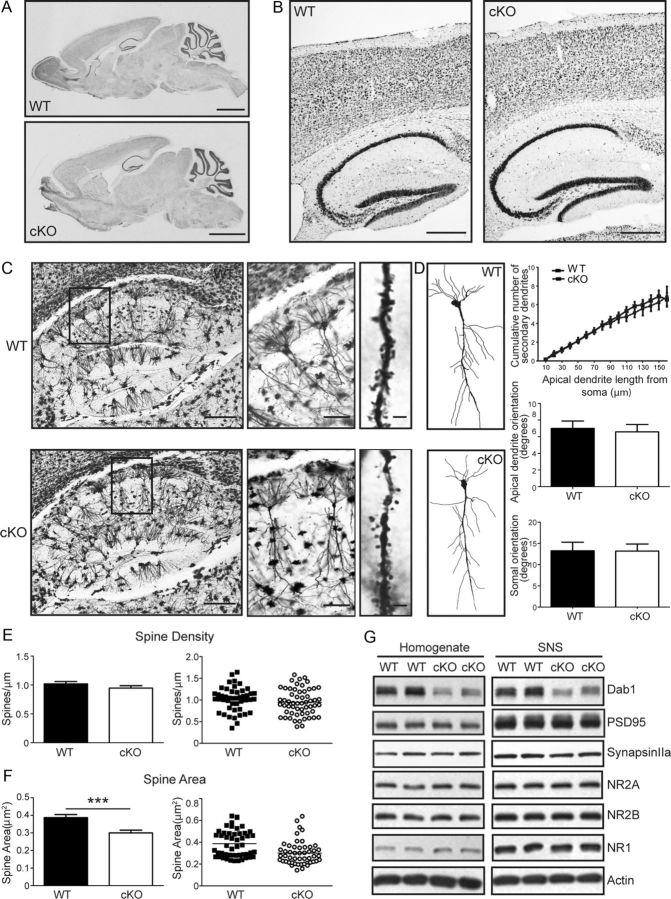
Figure 4.
Anatomy, dendrite morphology, and spine analysis in the Dab1 cKO hippocampus. A, B, Sagittal sections of 2-month-old WT and Dab1 cKO mice were stained with thionin. All main regions appear normal in whole brain images (A). Magnified images of the cortex and hippocampus also show no obvious defects in cellular layers (B). Scale bars: A, 2 mm; B, 200 μm. C, Images of Golgi-stained hippocampus from 2-month-old WT and cKO mice. Insets on the left were further magnified to show individual pyramidal neurons and their dendrites in area CA1 (middle). Representative z-stack images of secondary apical dendrites bearing spines are also shown (right). Scale bars: left, 300 μm; middle, 100 μm; right, 2 μm. D, Tracing and analysis of dendrite branching and neuronal orientation. Examples of traced WT and cKO pyramidal neurons in area CA1 are shown. Twenty-six WT and 17 cKO neurons from 4 to 5 mice per genotype were used for branching analysis; 40 WT and 34 cKO neurons from 4 to 5 mice per genotype were used for neuronal orientation analysis. No significant change in secondary dendrite branching or orientation of apical dendrites and cell body is apparent. E, F, Quantification of spine density (E) and area (F). There was no significant difference in spine density between WT and cKO neurons. However, spine area was significantly smaller in Dab1 cKO compared with WT mice (***p < 0.0001). G, Western blot analysis of Dab1 and synaptic protein markers in the homogenate and crude SNS fractions of WT and Dab1 KO hippocampus. The blots were probed sequentially or in parallel with antibodies against Dab1, postsynaptic PSD-95, NMDAR subunits NR1 and NR2A, and presynaptic synapsin IIa. Actin was used as a loading control. Although Dab1 levels were decreased in samples obtained from cKO mice, the levels of all analyzed synaptic proteins appear similar between genotypes (data from 5 to 6 mice per genotype).