Figure 8.
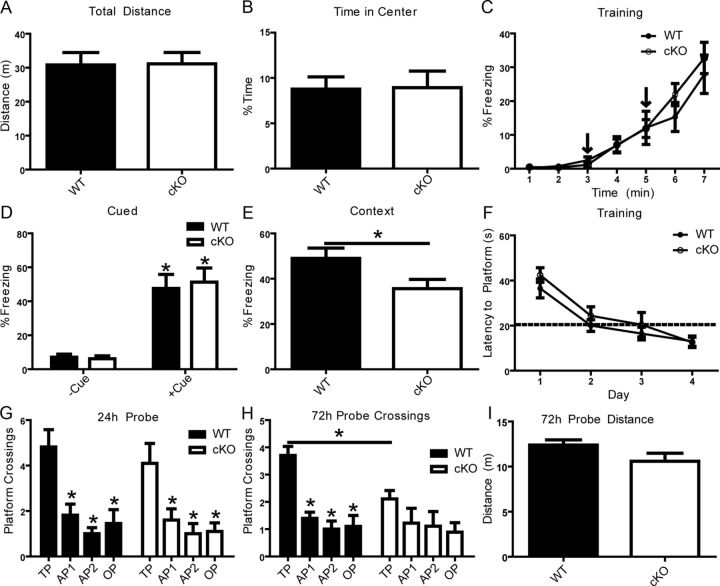
Normal fear associative learning requires Dab1. A, B, Differences in locomotor activity and anxiety were evaluated using a 30 min open-field test. The Dab1 cKO mice (n = 11) and WT controls (n = 11) exhibited similar levels of activity. Two-trial fear conditioning was used to determine associative learning at 24 h following two CS–US pairings. C, D, No differences were seen in freezing rates during training or in a novel context in the absence or presence of the CS (tone) when comparing WT and cKO mice. E, WT mice (n = 11) exhibited a greater conditioning to the context compared with Dab1 cKO (n = 11; *p < 0.05). F–I, Hidden-platform water maze was used to assess spatial learning and memory. No differences between WT and cKO were seen in latency to platform across 4 d of training (4 trials/d). A 60 s probe trial was conducted at 24 h post-training. No significant difference was found in the number of target platform (TP) crossings by WT (n = 11) versus Dab1 cKO mice (n = 10). Both genotypes crossed into the TP significantly more times than in other pseudo-platform areas (*p < 0.05). At 72 h, a probe trial revealed that WT mice crossed into the TP significantly more times than cKO and compared with other platform regions (*p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA using the Bonferroni's post hoc test). No difference was seen in distance traveled between the genotypes. OP, opposite platform; AP1, adjacent platform 1; AP2, adjacent platform 2.