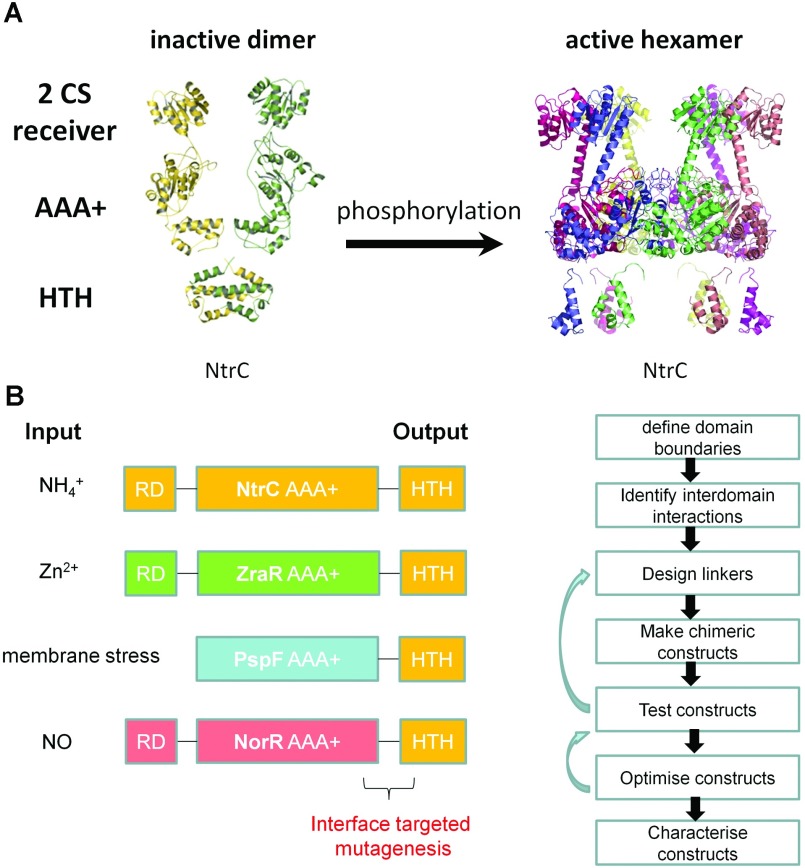
Figure 2. Engineering functional domain exchanged synthetic EBPs (enhancer-binding proteins) to rewire signalling networks.
(A) Structural model of the phosphorylation-induced conformational changes and oligomer assembly of NtrC (adapted with permission from [21,31]). The interfaces between the receiver domain and the AAA+ domain and that between the AAA+ domain and the HTH domain play important regulatory roles in various NtrC homologues through inter-domain allosteric control and determine transcription control stringency [32] (B) Engineering strategy for functional domain exchanged synthetic EBPs to rewire signalling networks. Engineered chimaeric EBPs are constructed by coupling the HTH DNA-binding domain of one EBP (e.g. NtrC) to the receiver and AAA+ domains of a non-cognate bEBPs such as ZraR (zinc), PspF (membrane stress), NorR (NO). The functional chimaera can then be selected out by interface-targeted mutagenesis by randomly mutating the linker region between the two coupled domains.