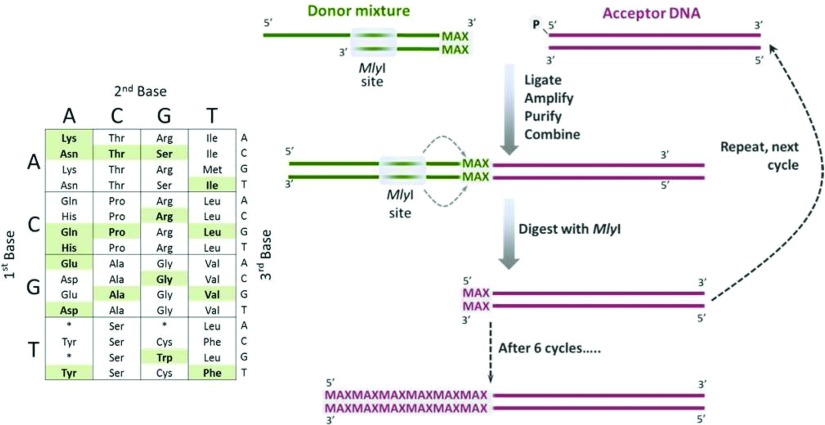
Figure 2. ProxiMAX methodology.
Double-stranded DNA donors, carrying the required ‘MAX’ codons at their termini, are ligated individually on to a double-stranded DNA acceptor sequence (phosphorylated at the required 5′ end only). The donors can take the form of partially double-stranded DNA (as shown), fully double-stranded DNA or hairpin oligonucleotides. After ligation, the products are amplified, purified, quantified and then combined in the required ratios. The combined product is digested with MlyI. The process is then repeated, using the digestion product from cycle 1 as the acceptor for the next round of ligation. Different sets of donors are cycled to prevent potential carry-over from one cycle to the next. The inset of the genetic code shows that any codons may be selected as ‘MAX’ codons, regardless of their sequence.