Figure 2. High-throughput genomic analysis spanning all regulatory checkpoints.
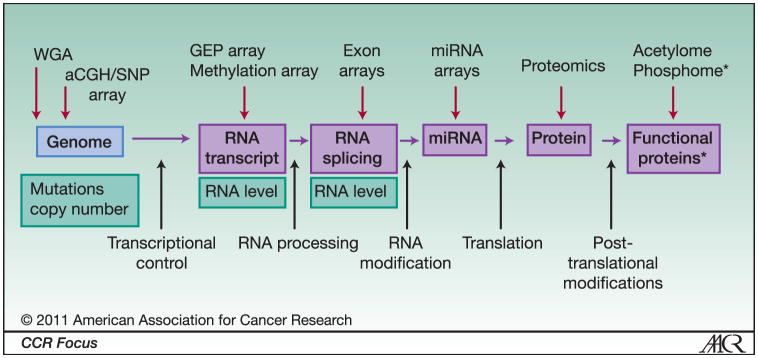
Genomic information is translated through various processes including post-translational protein modification (middle row). Abnormalities at these various levels potentially play a role in development of malignant transformation and behavior of the cancer cell (bottom row). Various high -throughput genomic analysis methods and arrays spanning all regulatory checkpoints are available to identify these various genomic abnormalities to develop an integrated approach that will lead to understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of cancer, identification of novel targets and therapies, development of personalized medicine, and predictive models for outcome. * protein modification such as phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiqiitination, sumoylation etc.
