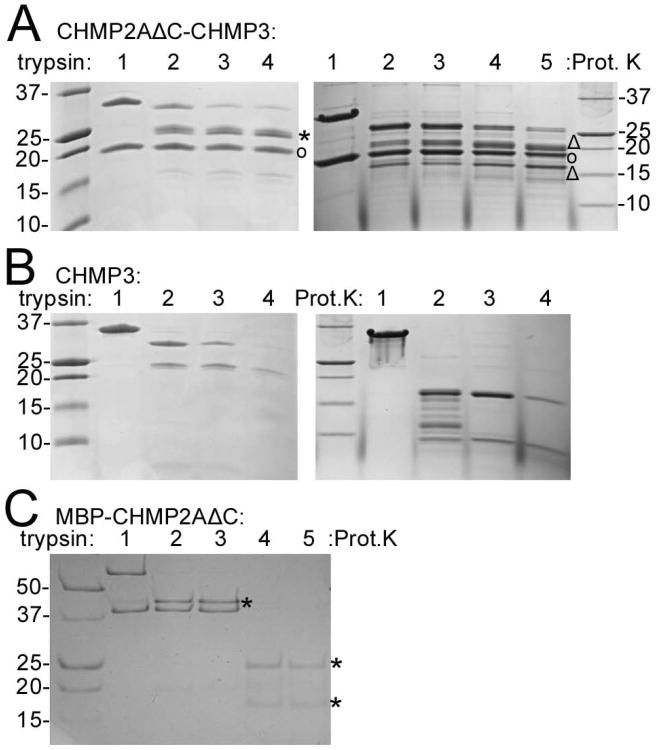
Figure 6. CHMP2AΔC-CHMP3 polymerization into tubes renders CHMP2A and CHMP3 protease resistant.
(A) Trypsin and proteinase K proteolysis of CHMP2AΔC-CHMP3 tubes. Right panel: lane 1, no trypsin; lanes 2-4 trypsin: CHMP2AΔC-CHMP3 tube ratios of 1:70; 1:35 and 1:20 (w/w), respectively. Right panel: lane 1, no proteinse K; lanes 2-5, proteinase K ratios of 1:500, 1:250, 1:100 and 1:50 (w/w), respectively. (CHMP2AΔC (°); CHMP3 bands produced by trypsin (*) and Proteinase K (Δ) digestion)
(B) Trypsin and proteinase K proteolysis of CHMP3. Right panel: lane 1, no trypsin; lanes 2-4, trypsin: CHMP3 ratios of 1:70, 1:35 and 1:20 (w/w), respectively.
(C) Trypsin and proteinase K proteolysis of MBP-CHMP2AΔC. Lane 1, no trypsin; lanes 2 and 3 trypsin/MBP-CHMP2AΔC ratios of 1:100 and 1:50 (w/w); lanes 4 and 5, proteinase K/MBP-CHMP2AΔC ratios 1:100 and 1:50 (w/w). (MBP bands after proteolysis (*)).