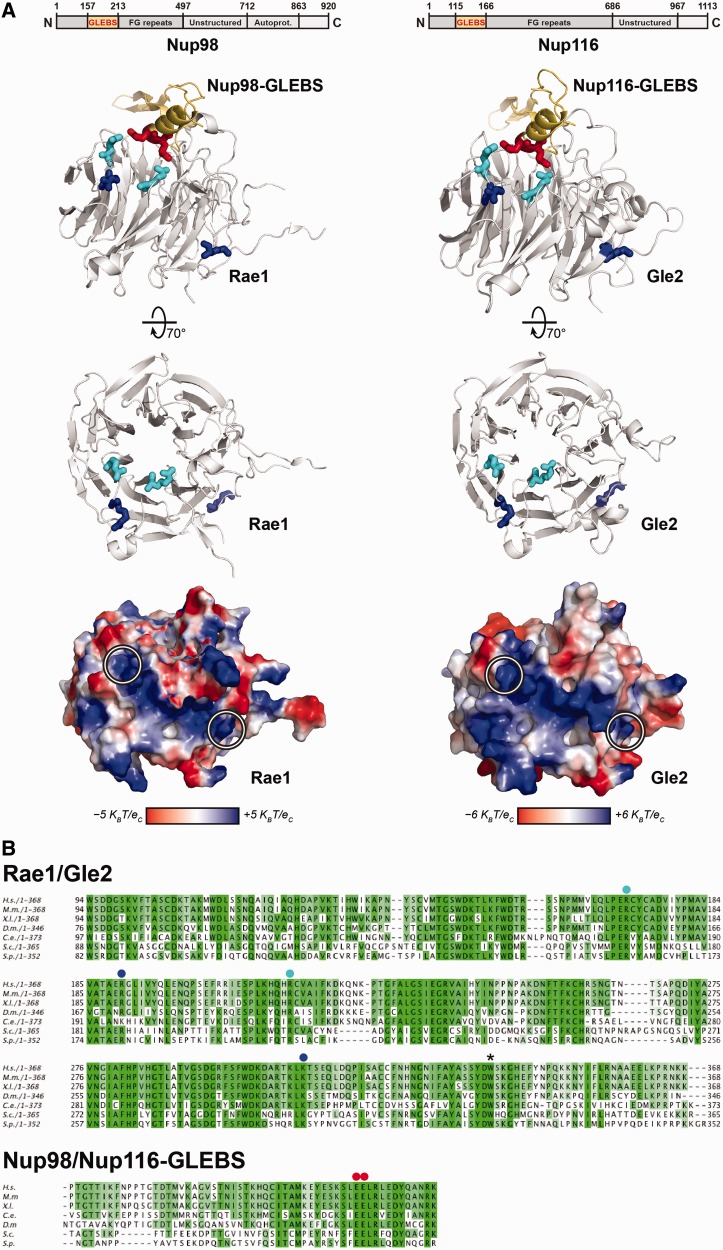
Figure 4.
Conserved interactions of the Rae1:Nup98-GLEBS crystal structure and the modeled Gle2:Nup116-GLEBS interface. (A) Top: Schematic representation of Nup98 and Nup116 domain organization. Residue numbers indicate the domain boundaries. Center: Ribbon representations of Rae1:Nup98-GLEBS (left) and Gle2:Nup116-GLEBS (right) complexes, visualized by PyMOL. Structure information of Rae1:Nup98-GLEBS was acquired from the Protein Data Bank (DOI:10.2210/pdb3mmy/pdb) (29). The structure modeling of Gle2:Nup116-GLEBS was performed by using PHYRE2 server (62). Of the 365 residues of Gle2, 339 residues, i.e. 93% of Gle2 primary sequence, could be modeled with high confidence using Rae1:Nup98-GLEBS as template. Conserved residues in the basic patch are indicated in blue. Conserved residues involved in making salt bridges in Rae1:Nup98-GLEBS or potentially involved in making salt bridges in Gle2:Nup116-GLEBS are indicated in cyan (in Rae1/Gle2) and red (in Nup98/Nup116). Bottom: Van der Waals surface representation of Rae1 and Gle2. The two conserved arginine and lysine residues located at the ends of the conserved basic patch are highlighted with white circles. KB, Boltzmann’s constant (1.381 × 10−23 JK−1); T, temperature (310 K); ec, elementary charge (1.602 × 10−19 C). (B) Top: Sequence alignment of Rae1 (partial) from Homo sapiens (H.s.), Mus musculus (M.m.), Xenopus laevis (X.l.), Drosophila melanogaster (D.m.), Caenorhabditis elegans (C.e.), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.c.) and Schizosaccaromyces pombe (S.p.) using ClustalW program (63). Bottom: Sequence alignment of the GLEBS domain of human Nup98 with its homologs from various organisms using ClustalW program. The overall sequence conservation at each position is shaded in a color gradient from light green (40% identity) to dark green (100% identity). Conserved residues (R186 and K305 in S.c. Gle2) that were mutated in gle2-patch allele are marked with blue dots. Conserved residues (R168 and R212 in S.c. Gle2) that were mutated in gle2-gis mutant are marked with cyan dots. Conserved residues (E154 and E155 in S.c. Nup116) of the Nup98-GLEBS that are involved in making salt bridges with Rae1 are marked with red dots. The asterisk indicates the conserved tryptophan mutated to a stop codon in the gle2-1 allele.