Fig. 2.
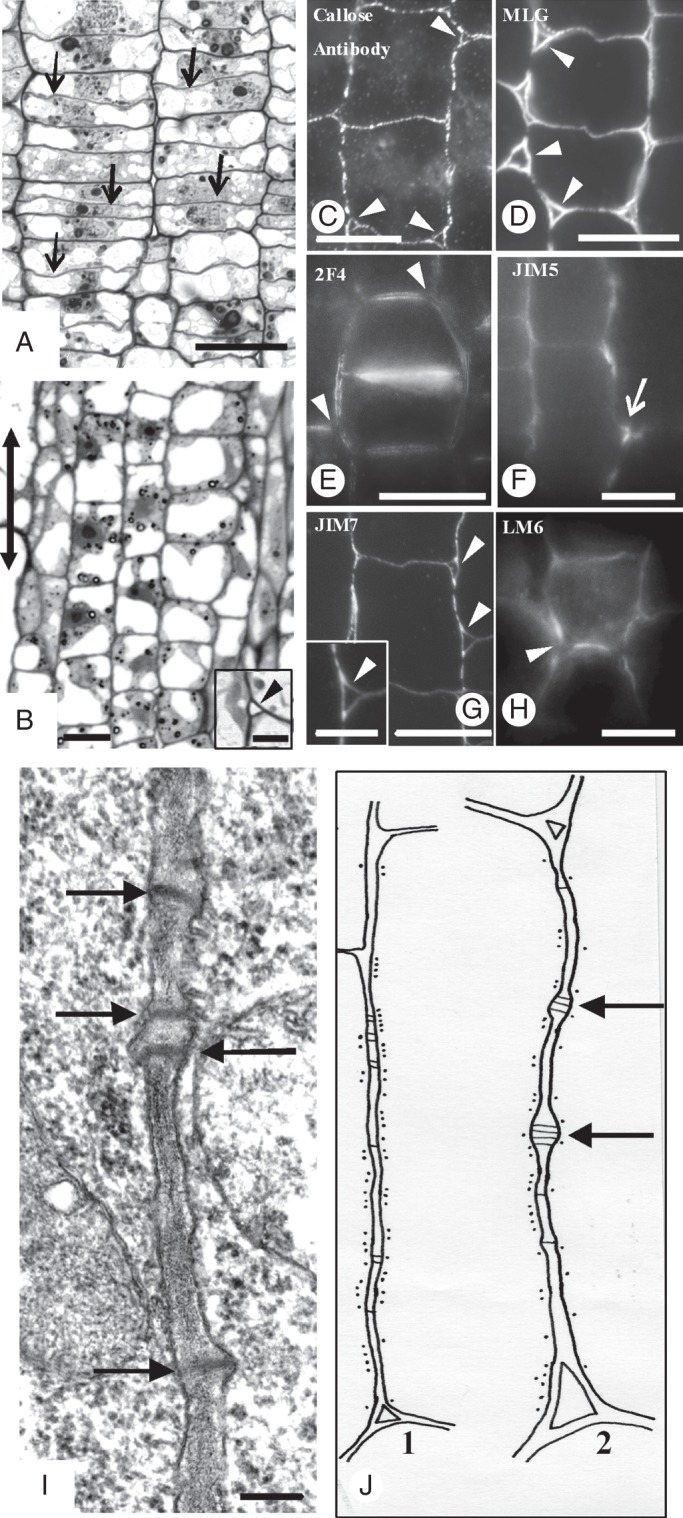
Micrographs of MC initials taken with a conventional light microscope (A, B), an epifluorescence microscope (C–H) and a TEM (I). (A, B) Paradermal semi-thin sections of MC initials located at the meristematic leaf zone (A) and the region just next to it (B). Arrows in (A) indicate the newly formed transverse cell walls, while the double arrow in (B) indicates the leaf axis in (A–J). (Inset in B) Triangular intercellular space (arrowhead) generated at the junction site of three MC initials. (C–H) Localization of callose (C), MLGs (D) and pectin epitopes (E–H) in cell walls of MC initials. Arrowheads indicate intercellular spaces formed at the junction sites of three or more MC initials. Arrow in (F) shows the junction of a transverse with a longitudinal MC wall. (C, D, G) Immunolabelling in LRW sections. (E, F, H) Immunolabelling in hand-made sections. (I) Longitudinal cell wall portion of an MC initial. Arrows mark plasmodesmata. Scale bars: (A–H) = 10 μm; (I) = 200 nm; (B inset) = 3 μm; (G inset) = 5 µm. (J) Diagram showing the distribution of cortical microtubules along a longitudinal cell wall of a MC initial (J1) and a nascent MC (J2). Black dots represent microtubules; black lines represent plasmodesmata. Arrows show young plasmodesmata clusterings.
